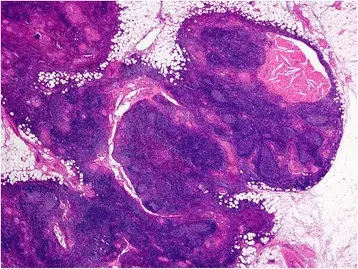
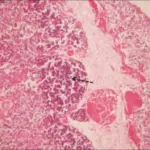
Thymic hyperplasia is increased thymic tissue.
What is the Pathology of Thymic Hyperplasia?
The pathology of thymic hyperplasia is:
-Etiology: The cause of thymic hyperplasia may be stress, medication use, endocrine disorders, or tumor.
-Pathogenesis: Increased thymic cells.
-Morphology: Increased size of thymus.
-Histology: Cellular thymocytes.
How does Thymic Hyperplasia Present?
Patients with thymic hyperplasia are typically children of either gender. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with thymic hyperplasia are not remarkable.
How is Thymic Hyperplasia Diagnosed?
Thymic hyperplasia is diagnosed by physical exam, imaging, and biopsy.
How is Thymic Hyperplasia Treated?
Thymic hyperplasia may resolve on its own, or be treated surgically.
What is the Prognosis of Thymic Hyperplasia?
The prognosis of thymic hyperplasia is good.