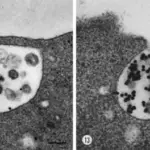
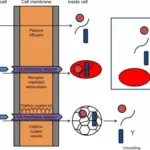
Transcytosis is a type of transcellular transport in which various macromolecules are transported across the interior of a cell.
What is Transcytosis?
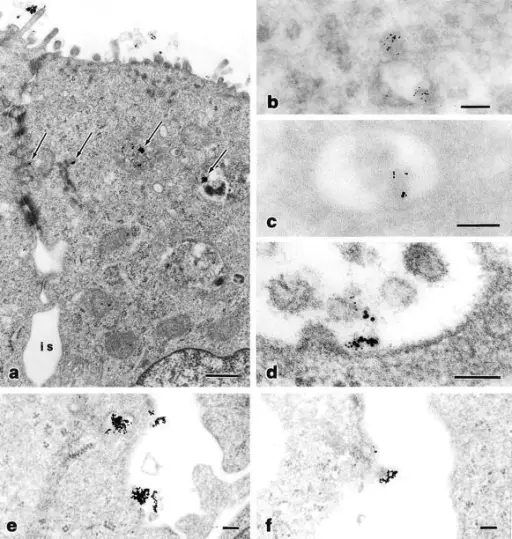
Transcytosis. Analysis of transcytosis of LPS by transmission electron microscopy. (a, e, and f) Cross-section of a polarized T84 cell monolayer, after internalization of LPS-coated gold particles at the apical pole. Panel a shows apical villi, tight junctions, inter(para)cellular space (i.s.), and basally positioned nucleus. LPS-coated particles primarily localize to vesicles in the apical region of the polarized cell (arrows), some of them in close proximity of the lateral region opposing the paracellular space. e and f show the intercellular region below the tight junctions, with LPS appearing within basolateral endosomes adjacent to the lateral membrane and proceeding to exocytosis into the paracellular space. (b–d) Double immunogold labeling of LPS (10 nm gold particles) and the transferrin receptor (5 nm gold particles). Panel b shows two adjacent vesicles, one containing the transferrin receptor alone (bottom) and one (top) containing both LPS and the transferrin receptor. Panels c and d show multimembranous vesicles containing both LPS and the transferrin receptor. Bars: (a) 500 nm; (b–f) 100 nm. Trafficking of Shigella lipopolysaccharide in polarized intestinal epithelial cells.
Beatty WL, Méresse S, Gounon P, Davoust J, Mounier J, Sansonetti PJ, Gorvel JP - The Journal of cell biology (1999). Not Altered. CC.