Transfusion associated circulatory overload is when transfusion as caused fluid overload in the circulatory system and characterized by pulmonary edema.
What is the Pathology of Transfusion Associated Circulatory Overload?
The pathology of transfusion associated circulatory overload is: the disease that occurs after or during blood transfusion that lead to fluid overload in the pulmonary system.
-Etiology: The cause of transfusion associated circulatory overload is excess blood transfusion, underlying cardiogenic disease and renal disease.
-Genes involved: None.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to transfusion associated circulatory overload is wen the patient has ana underlying condition that predisposes them to fluid overload. Also when the transfusion rate is not well monitored and the amount being transfused is excess.
-Morphology: NA.
-Histology: NA.
How does Transfusion Associated Circulatory Overload Present?
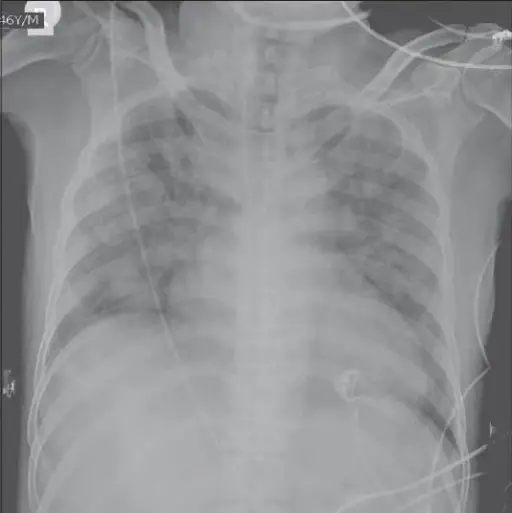
Patients with transfusion associated circulatory overload typically all gender present at age range of the most elderly. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with transfusion associated circulatory overload include acute respiratory distress, increased blood pressure, chest pain, tachycardia, and acute pulmonary edema.
How is Transfusion Associated Circulatory Overload Diagnosed?
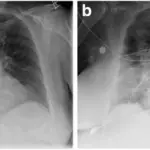
Transfusion associated circulatory overload is diagnosed by physical examination of the symptoms, ranges of the brain natriuretic peptide, chest X-ray and history taking.
How is Transfusion Associated Circulatory Overload Treated?
Transfusion associated circulatory overload is treated by cessation of the transfusion, upright positioning of the patient, intubation,, oxygenation, splitting of the blood into tolerable portions.
What is the Prognosis of Transfusion Associated Circulatory Overload?
The prognosis of transfusion associated circulatory overload is poor since the reaction if very fatal and can lead to death immediately.