Typhoid fever is a bacterial infection that can spread throughout the body, affecting many organs. Without prompt treatment, it can cause serious complications and can be fatal. It’s caused by a bacterium called Salmonella typhi.
What is the Pathology of Typhoid Fever?
The pathology of typhoid fever is:
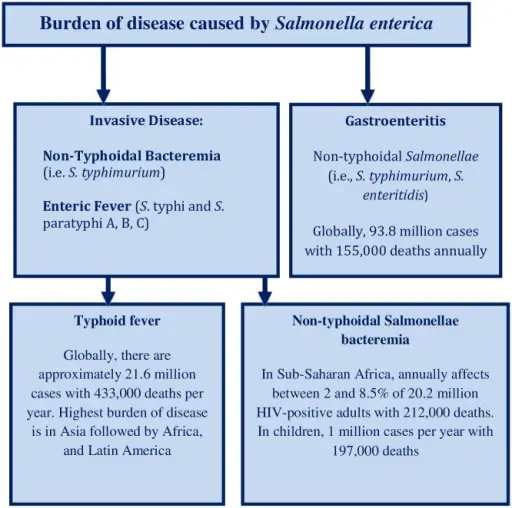
-Etiology: The cause of typhoid fever is Salmonella enterica.
-Genes involved: None.
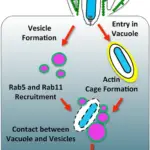
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to typhoid fever are: the intake of bacteria with contaminated food consequently ingested and the infectious bacteria taken up by macrophages towards lymph nodes where they multiply and enter blood stream at the end of incubation period hence causing fever.
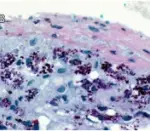
-Histology: The histology associated with typhoid fever shows sinusoids are enlarged and distended by large collections of macrophages and reticuloendothelial cells.
How does Typhoid Fever Present?
Patients with typhoid fever typically in all genders at any age. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with typhoid fever include: High fever, headache, Stomach pain, Constipation or diarrhea.
How is Typhoid Fever Diagnosed?
Typhoid fever is diagnosed analysing samples of blood, stool, or urine.
How is Typhoid Fever Treated?
Typhoid fever is treated by Ciprofloxacin, Azithromycin, Ceftriaxone
What is the Prognosis of Typhoid Fever?
The prognosis of typhoid fever is good. Generally, untreated typhoid fever carries a mortality rate of 15%-30%. In properly treated disease, the mortality rate is less than 1%.