Urticaria is a common ailment of the skin localized mast cell degranulation and subsequent dermal microvascular hyperpermeability, ending in pruritic edematous plaques (wheals).
What is the Pathology of Urticaria?
The pathology of urticaria is:
-Etiology: The cause of urticaria is an infection, allergen, some drugs, exposure to latex, pregnancy, idiopathic.
-Genes involved: None.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to urticaria; results from the antigen-induced release of vasoactive mediators from mast cell granules via sensitization with specific immunoglobulin E (IgE) antibodies following the exposure.
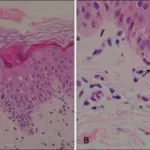
-Morphology: The morphology associated with urticaria shows lesions varying from trivial, pruritic papules to big edematous plaques.
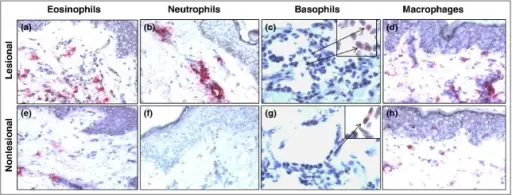
-Histology: The histology associated with urticaria shows sparse superficial perivenular infiltrate of mononuclear cells rare neutrophils and eosinophils.
How does Urticaria Present?
Patients with urticaria typically slightly more common in males than females present at an age range of 20 to 40 years. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with urticaria include usually lesions fading within hours, palpable wheals small, pruritic papules, and large erythematous plaques.
How is Urticaria Diagnosed?
Urticaria is diagnosed through the clinical presentation, laboratory studies, CBC count, ESR, antinuclear antibody (ANA), and thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), and biopsy.
How is Urticaria Treated?
Urticaria is treated through the systemic management of symptoms.
What is the Prognosis of Urticaria?
The prognosis of urticaria is good for acute urticaria as it is self-limiting.