Varicella-Zoster virus infectious neuropathy is a common viral infection to the peripheral nervous symptoms.
What is the Pathology of Varicella-Zoster Virus Infectious Neuropathy?
The pathology of varicella-zoster virus infectious neuropathy is:
-Etiology: The cause of varicella-zoster virus infectious neuropathy is Varicella-Zoster Virus Infectious complication.
-Genes involved: NA.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to varicella-zoster virus infectious neuropathy results from viral infections of the peripheral nervous system. Latent infection of neurons in the sensory ganglia of the spinal cord and brain stem follows chickenpox. Reactivation causes painful, vesicular skin outbreaks at the site of sensory dermatomes.
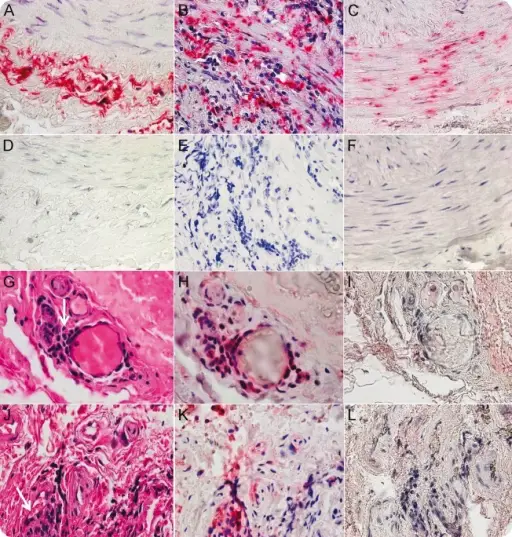
-Morphology: The morphology associated with varicella-zoster virus infectious neuropathy shows necrosis and hemorrhage at the site.
-Histology: The histology associated with varicella-zoster virus infectious neuropathy shows inflammatory insinuates of mononuclear.
How does Varicella-Zoster Virus Infectious Neuropathy Present?
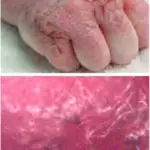
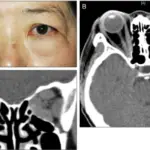
Patients with varicella-zoster virus infectious neuropathy typically have gender prevalence present at an age range of childhood. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with varicella-zoster virus infectious neuropathy include peripheral facial weakness, external auditory canal rush.
How is Varicella-Zoster Virus Infectious Neuropathy Diagnosed?
Varicella-zoster virus infectious neuropathy is diagnosed through the clinical presentation, laboratory studies, CSF analysis presence of anti-VZV antibodies.
How is Varicella-Zoster Virus Infectious Neuropathy Treated?
Varicella-zoster virus infectious neuropathy is treated through intravenous acyclovir therapy, VZV immune globulin, and VZV vaccine.
What is the Prognosis of Varicella-Zoster Virus Infectious Neuropathy?
The prognosis of varicella-zoster virus infectious neuropathy is fair.