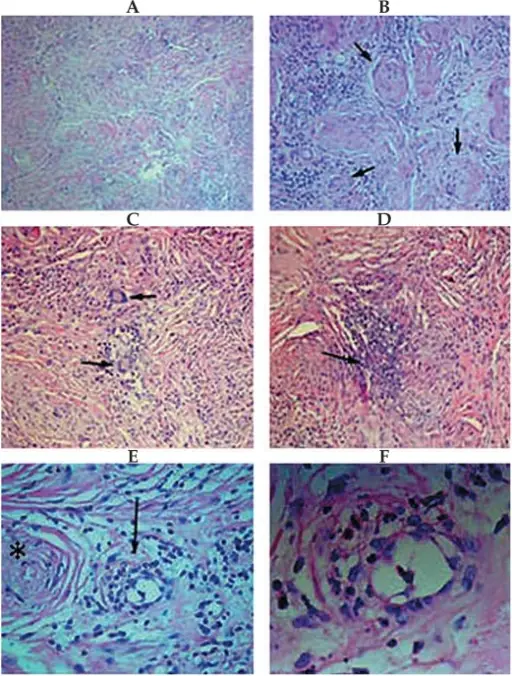
Histopathological examination of the specimen shows evidence of granulomatous vasculitis: (A) Fibrotic and collagenized vascular tufts in which the lumens are occluded with infiltration of acute and chronic inflammatory cells within the collagenous stroma (Hematoxylin & Eosin, ×100). (B) Higher magnification shows occluded vascular lumens (arrows) surrounded by infiltration of inflammatory cells (Hematoxylin & Eosin, ×200). (C) Granulomatous inflammation accompanied by infiltration of Langhans cells, a variety of multinucleated giant cells (Hematoxylin & Eosin, ×200). (D) Small area of necrosis surrounded by acute inflammatory cells in the background stroma (Hematoxylin & Eosin, ×200). (E) Polymorphonuclear cells and eosinophils have infiltrated the vascular wall, compatible with vasculitis (arrow). The lumen of an occluded vessel is visible adjacent to the vasculitis on the left side of the image (asterisk) (Hematoxylin & Eosin, ×400). (F) Higher magnification of the vasculitis shown in figure E (Hematoxylin & Eosin, ×1000).Bilateral orbital mass lesions: a presentation of Wegener's granulomatosis.
Aletaha M, Tavakoli M, Kanavi MR, Hashemlou A, Roghaei S - Journal of ophthalmic & vision research (2011). Not Altered. CC.
Vasculitis is inflammation of the walls of the blood vessels.
Examples of vasculitis include:
- Infectious vasculitis
- Noninfectious vasculitis
