Verrucae is a common lesion of children and adolescents, although they may be encountered at any age.
What is the Pathology of Verrucae?
The pathology of verrucae is:
-Etiology: The cause of verrucae is human papillomaviruses.
-Genes involved: None.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to verrucae; caused by various types of HPV viruses, different types of HPV not only have different morphologic lesions but also have variable oncogenic potential. Acquired through direct contact or autoinoculation. Usually undergo spontaneous regression.
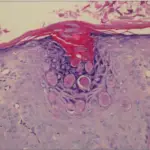
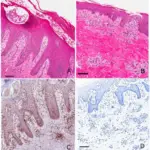
-Morphology: The morphology associated with verrucae shows that it defers according to the type. gray white to tan, flat to convex for Verruca vulgaris. Flat, smooth, tan macules for verruca plana.
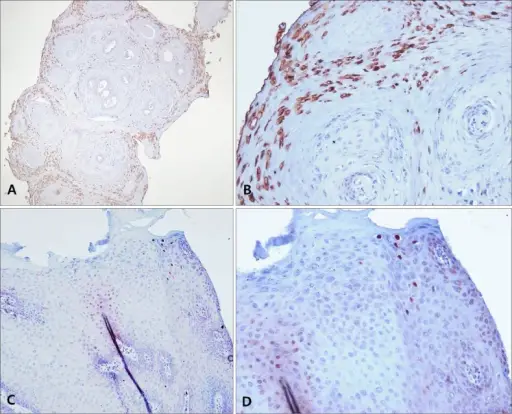
-Histology: The histology associated with verrucae shows epidermal hyperplasia, cytoplasmic vacuolization, numerous viral particles within nuclei, keratohyalin granules, and jagged eosinophilic intracytoplasmic keratin aggregates.
How does Verrucae Present?
Patients with verrucae typically has no gender prevalence, present at the age range of any age. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with verrucae include multiple nodules, scaly lesions.
How is Verrucae Diagnosed?
Verrucae are diagnosed through clinical examination and physical findings. Laboratory studies; immunohistochemical detection for HPV structural proteins, PRC for viral DNA testing.
How is Verrucae Vulgaris Treated?
Verrucae are treated through treatment for symptoms, medical care topical agents, systemic antiviral, vitamin A derivatives, immunotherapy.
What is the Prognosis of Verrucae?
The prognosis is verrucae good.