Viral hepatitis is an infection that causes liver inflammation and damage
Examples of viral hepatitis include:
- Hepatitis A virus
- Hepatitis B virus
- Hepatitis C virus
- Hepatitis D virus
- Hepatitis E virus
What is Hepatitis A Virus?
Hepatitis A virus is an inflammation transmitted through ingestion of contaminated food and water or direct contact with an infectious person.
What is Hepatitis B Virus?
Hepatitis B virus is a vaccine-preventable liver infection spread when blood, semen, or other body fluids from a person infected with the virus enters the body of someone who is not infected.
What is Hepatitis C Virus?
Hepatitis C virus is a liver infection spread through contact with blood from an infected person.
What is Hepatitis D Virus?
Hepatitis D virus is an infection that causes the liver to become inflamed.
What is Hepatitis E Virus?
Hepatitis E virus is a liver infection spread mainly through the fecal-oral transmission route.
What is the Pathology of Viral Hepatitis?
The pathology of viral hepatitis is:
-Etiology: The cause of viral hepatitis a viral infection.
-Genes involved: None.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to viral hepatitis as follows:
- Hepatitis A: Unknown.
- Hepatitis B: Interaction of the virus and the host immune system.
- Hepatitis C: Host immunity and metabolic changes including oxidative stress, insulin resistance, and hepatic steatosis.
- Hepatitis D: Interferon-α signaling inhibition, HDV-specific T-lymphocyte activation, and cytokine responses, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha and nuclear factor kappa B signaling.
- Hepatitis E: poorly understood and unspecific.
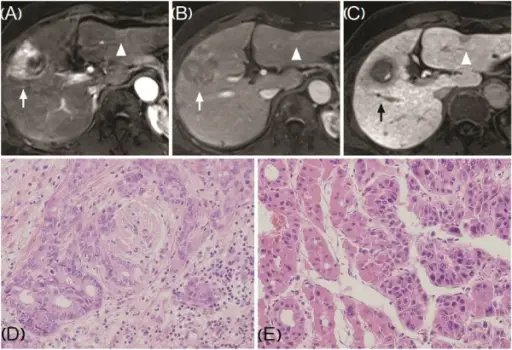
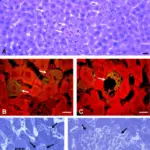
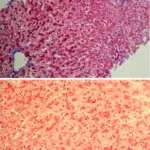
-Histology: The histology associated with viral hepatitis may show confluent necrosis, bridging necrosis, necrosis of entire lobules, and periportal necrosis.
How does Viral Hepatitis Present?
Patients with viral hepatitis typically affect males present in the age range of 35-55. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with acute HAV infection are marked by several weeks of malaise, anorexia, nausea, vomiting, and elevated aminotransferase levels. HBV and HCV are asymptomatic, however, the chronic HBV and HCV show fatigue. The HDV and HEV show the same clinical feature too.
How is Viral Hepatitis Diagnosed?
Viral hepatitis is diagnosed through a blood test.
How is Viral HepatitisTreated?
Viral hepatitis is treated by resting, resolving symptoms (pegylated interferon and ribavirin), and maintaining an adequate intake of fluids.
What is the Prognosis of Viral Hepatitis?
The prognosis of viral hepatitis A is good with an overall mortality of 0.02%, HBV is good as patients recover fully, HCV is fair with the clear virus within 6 months, HDV and HEV are good and patients recover fully.
| Viral Hepatitis | Hepatitis A | Hepatitis B | Hepatitis C | Hepatitis D | Hepatitis E |
| Transmission | Fecal-oral | blood | blood | blood | Fecal-oral |
| Incubation | 15-45 days | 45-160 days | 15-150 days | 30-60 days | 15-60 days |
| Treatment | No specific treatment | Antiviral medications | Antivirals, Combination drugs | No known treatments | No specific antiviral therapy |
| Prognosis | Good | Good | Fair | Good | Good |