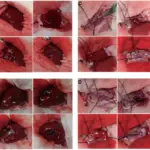
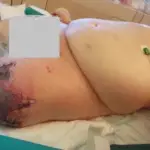
Warfarin is an anticoagulant that works by decreasing the clotting ability of blood.
What is Warfarin Toxicity?
Warfarin toxicity is when warfarin levels are excessively high.
What is the Pathology of Warfarin Toxicity?
The pathology of warfarin toxicity is:
-Etiology: The cause of warfarin toxicity is too much warfarin.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to warfarin toxicity is excessive warfarin.
How does Warfarin Toxicity Present?
Patients with warfarin toxicity typically are either males or females present in the age range of all age groups. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with warfarin toxicity may include bleeding.
How is Warfarin Toxicity Diagnosed?
Warfarin toxicity is diagnosed with a thorough physical examination, medical review, and blood tests such as INR, PT, and BT.
How is Warfarin Toxicity Treated?
Warfarin toxicity is treated with vitamin K, fresh frozen plasma, or protamine sulfate depending on the clinical implications and the urgency needed to reverse warfarin toxicity.
What is the Prognosis of Warfarin Toxicity?
The prognosis of warfarin toxicity is fair when properly treated.