White blood cell pathology is a blood disorder in which the white blood cells are either abnormally low (leukopenia) or abnormally high (leukocytosis). There are two broad categories which include leukopenias and proliferative disorders (leukocytosis). The proliferation of white blood cells may be malignant or reactive.
WHAT IS WHITE BLOOD CELL PATHOLOGY?
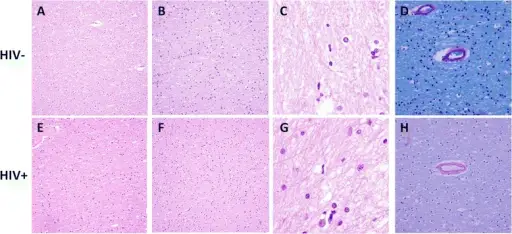
Representative formalin-fixed paraffin embedded autopsy brain frontal lobe tissue from HIV- (a-d) and HIV+ (e-h) cases stained with hematoxylin and eosin (a-c, e-g) or luxol fast blue and periodic acid-Schiff (d, h). A minority of HIV+ and HIV- cases were histologically unremarkable (a, e). Many HIV+ and HIV- cases exhibited mild histopathologic abnormalities including hypercellular white matter (b, f), increased rod cells (microglia) (c, g), and/or moderately thickened blood vessels (d, h). Original magnification 200× (a-b, e-f), 400× (d, h), and 1000× (c, g). Brain and liver pathology, amyloid deposition, and interferon responses among older HIV-positive patients in the late HAART era: BMC Infectious Diseases. Not altered. CC.