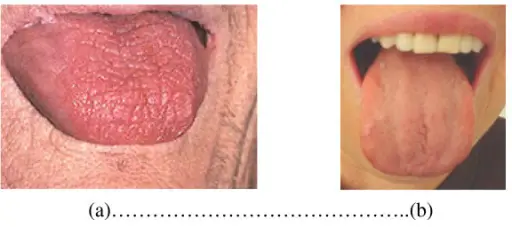
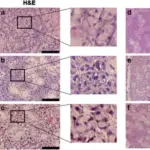
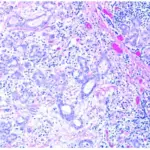
Xerostomia is defined as a dry mouth resulting from reduced or absent saliva flow. Xerostomia is commonly associated with Sjogren’s syndrome.
What is the Pathology of Xerostomia?
The pathology of xerostomia is:
-Etiology: Xerostomia may be caused by autoimmune, traumatic, or drug related conditions.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to xerostomia imay be immune related issues, or suppression from the CNS, or muscarinic or adrenergic receptor stimulation.
-Histology: The histology associated with xerostomia shows lymphoid infiltration with germinal centers, acinar atrophy, and interstitial fibrosis.
How does Xerostomia Present?
Patients with xerostomia typically are middle aged females. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with xerostomia include often dry mouth, dry eyes, and coughing.
How is Xerostomia Diagnosed?
Xerostomia is diagnosed based on physical exam, and lab tests for autoimmune conditions.
How is Xerostomia Treated?
Xerostomia is treated by the identification and resolution of the underlying cause.
What is the Prognosis of Xerostomia?
The prognosis of xerostomia is good.