Luteal cysts are a type of functional ovarian cyst that results when a corpus luteum fails to regress following the release of an ovum.
What is the Pathology of Ovarian Luteal Cysts?
The pathology of ovarian luteal cysts is:
-Etiology: The cause of ovarian luteal cysts is hormonal imbalance, pregnancy, endometriosis, previous cysts, and pelvic infection.
-Genes involved: CGB5 gene.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to ovarian luteal cysts are: The ruptured follicle begins producing large quantities of estrogen and progesterone in preparation for conception. If a pregnancy doesn’t occur, the corpus luteum usually breaks down and disappears. It may, however, fill with fluid or blood, causing the corpus luteum to expand into a cyst, and stay in the ovary.
-Morphology: The morphology associated with ovarian luteal cysts shows serous or hemorrhagic contents.
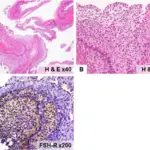
-Histology: The histology associated with ovarian luteal cysts shows convoluted cystic lining, polygonal shaped Granulosa cells.
How does Ovarian Luteal Cysts Present?
Patients with ovarian luteal cysts typically females at reproductive age or during pregnancy. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with ovarian luteal cysts include: pelvic pain, bloating, weight gain, painful intercourse, painful menstruation, breast tenderness.
How is Ovarian Luteal Cysts Diagnosed?
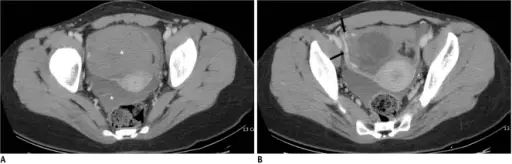
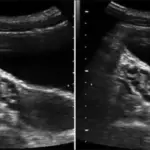
Ovarian luteal cysts is diagnosed by: pelvic ultrasound, hormonal tests, laparoscopic procedures.
How is Ovarian Luteal Cysts Treated?
Ovarian luteal cysts is treated by: hormonal contraceptives, prostaglandin F2α, surgical removal.
What is the Prognosis of Ovarian Luteal Cysts?
The prognosis of ovarian luteal cysts is good. They will go away on their own without treatment.