Cell Death Pathology Study Guide
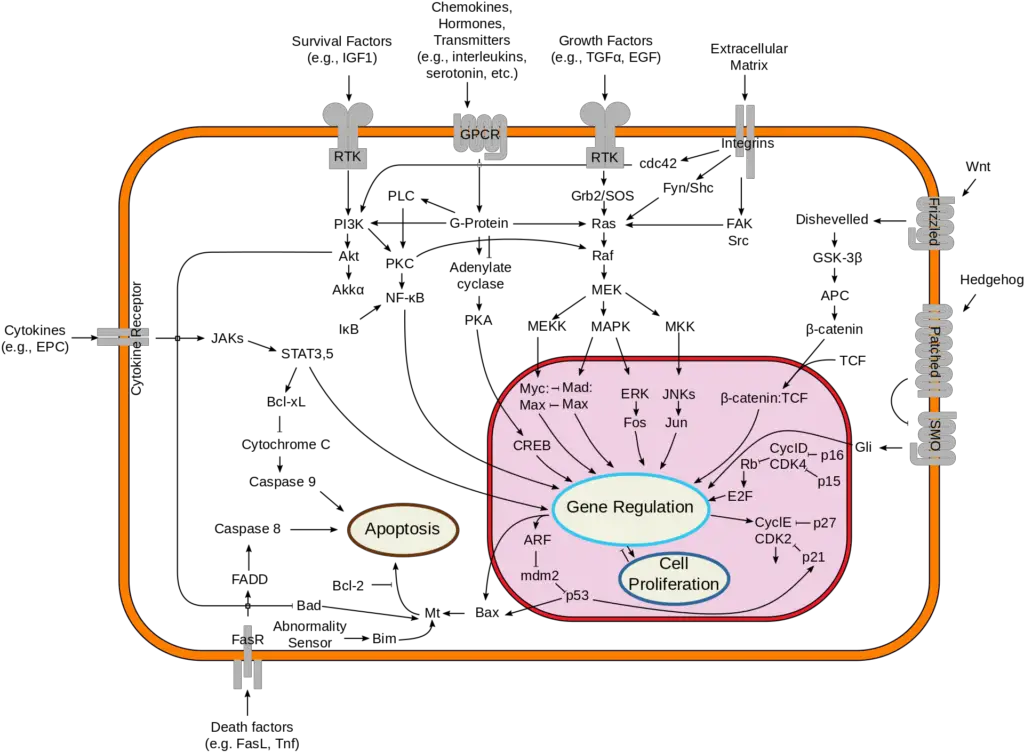
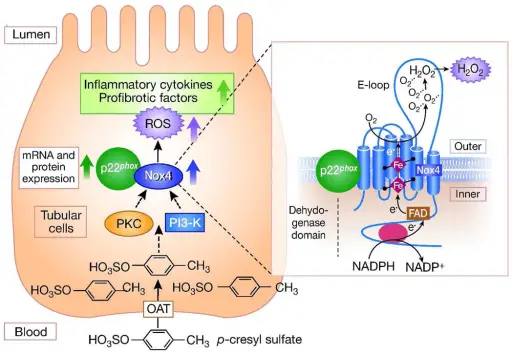
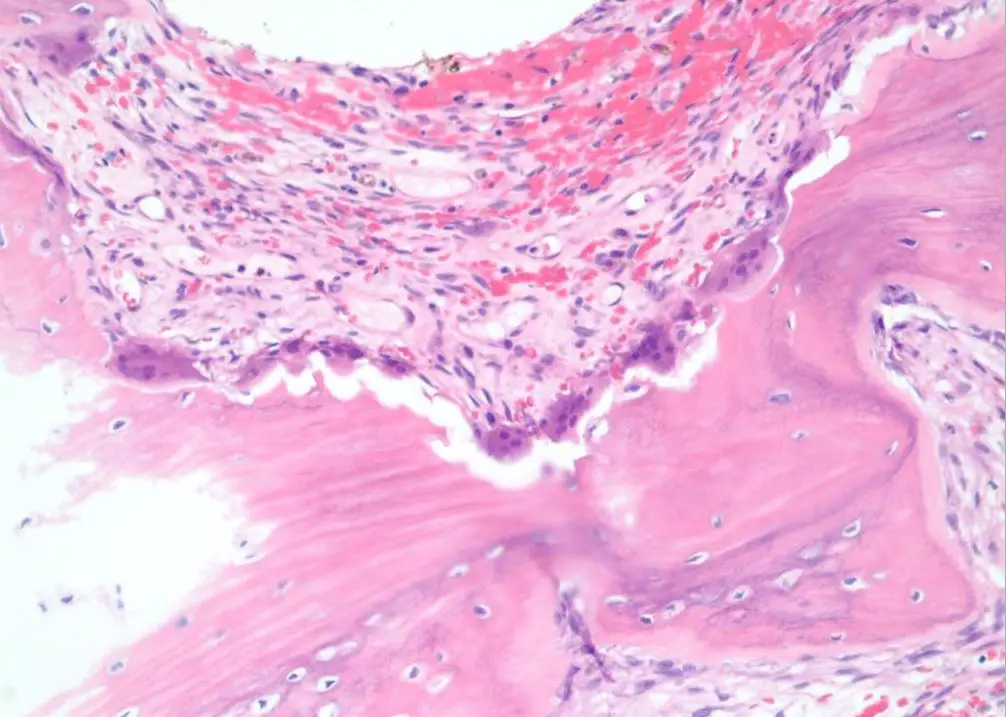
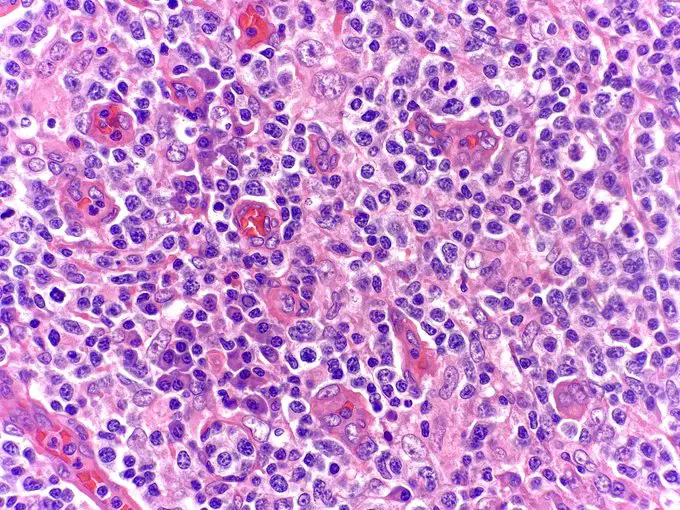
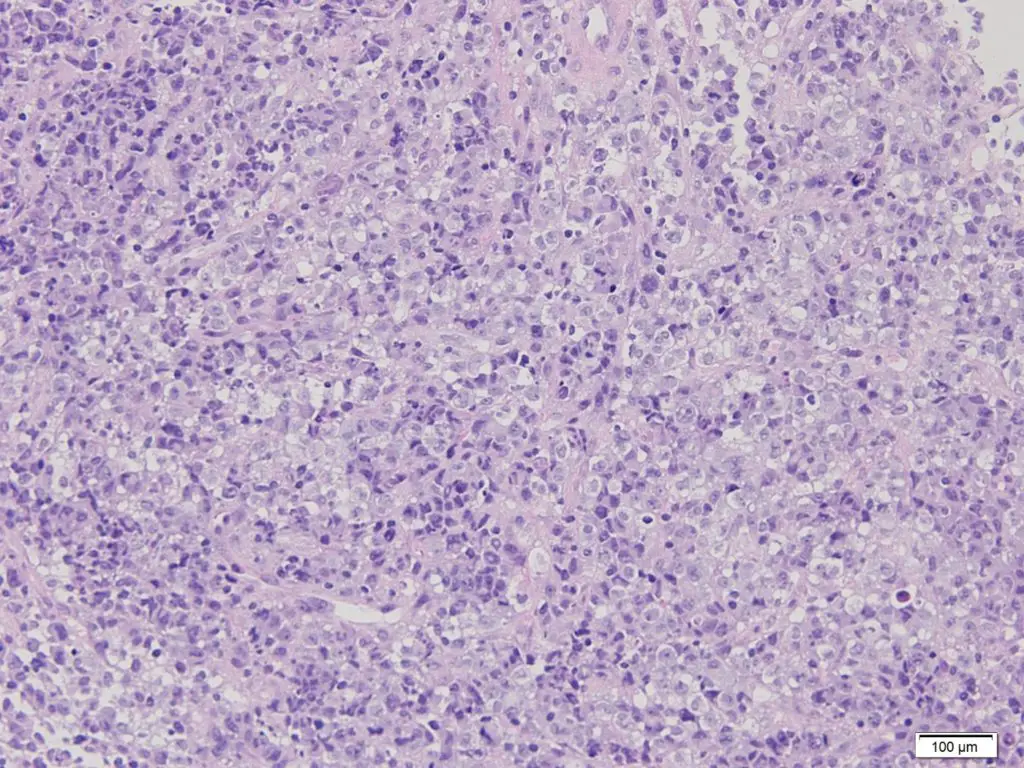
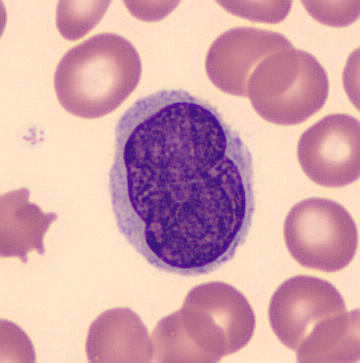
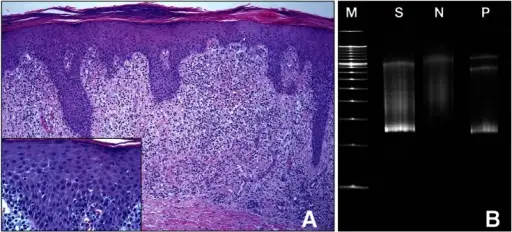
Cell Death Cell Death Pathology Video The hallmarks of cell death is loss of the cell nucleus. The mechanism of nuclear loss in cell death includes: Pyknosis Karyorrhexis Karyolysis Pyknosis means nuclear condensation. Karyorrhexis means fragmentation. Karyolysis means dissolution. There…