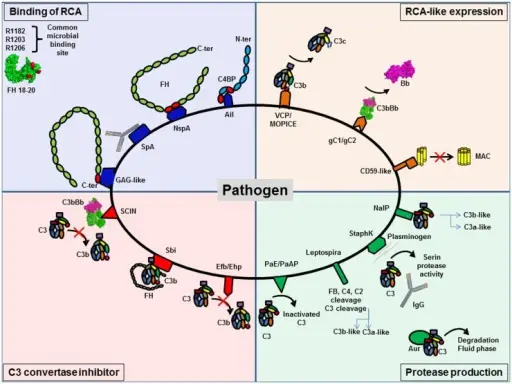
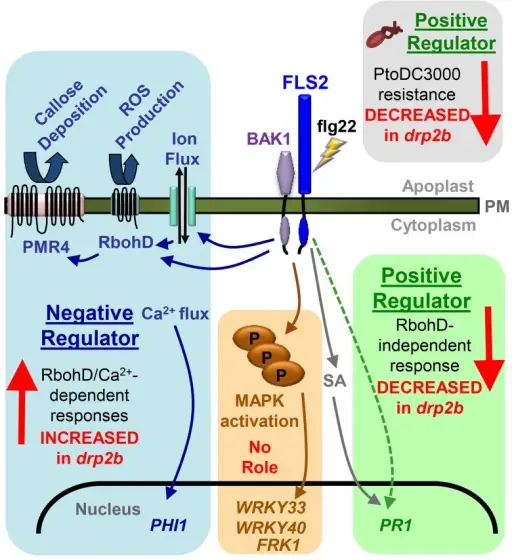
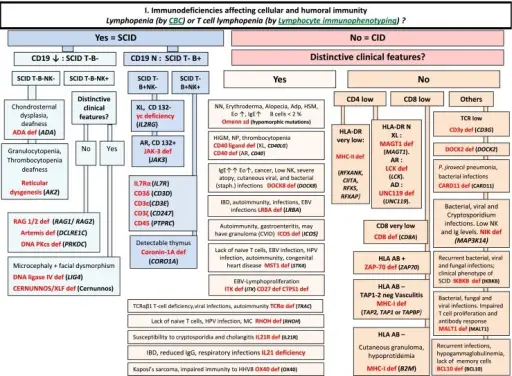
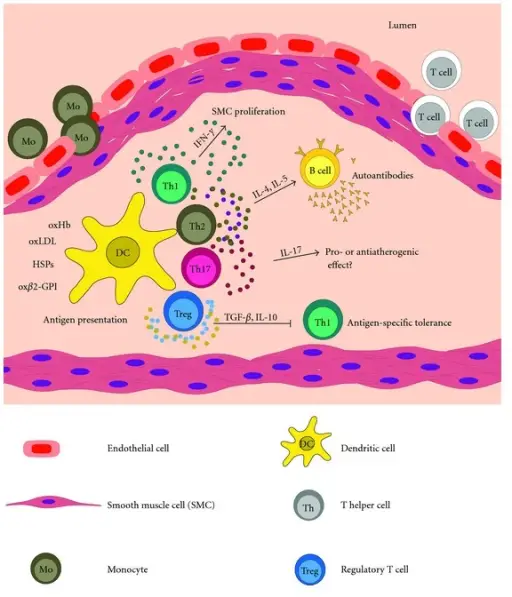
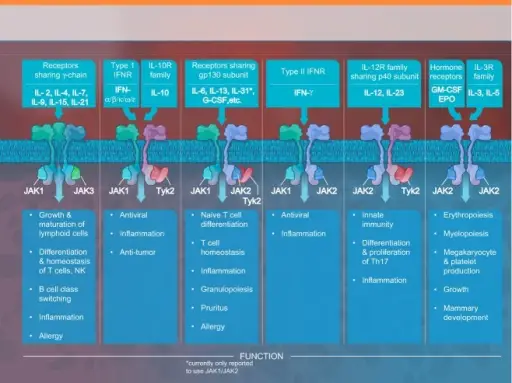
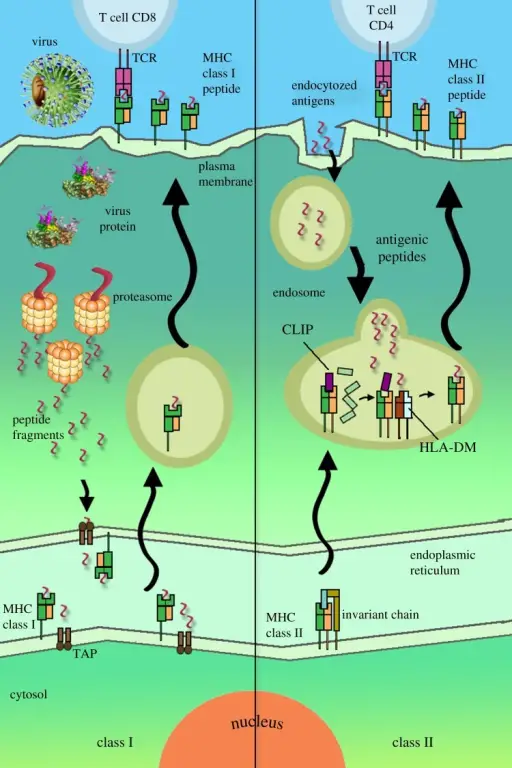
What are Immunodeficiencies Associated with Systemic Diseases?
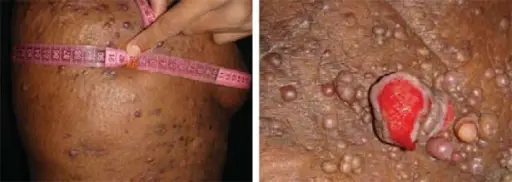
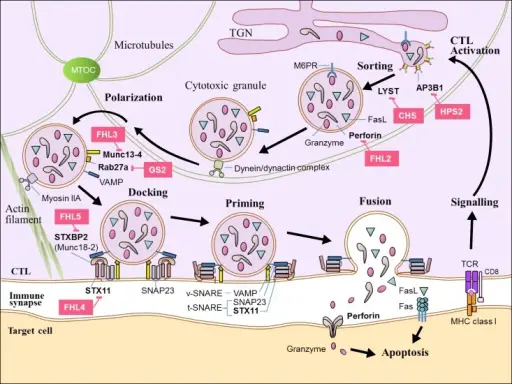
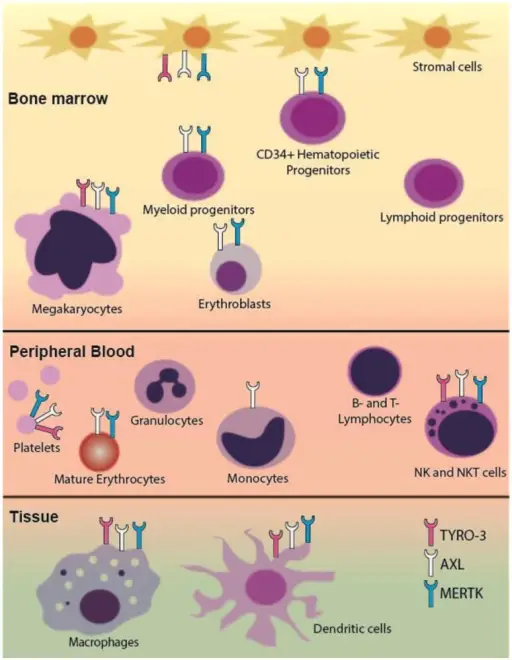
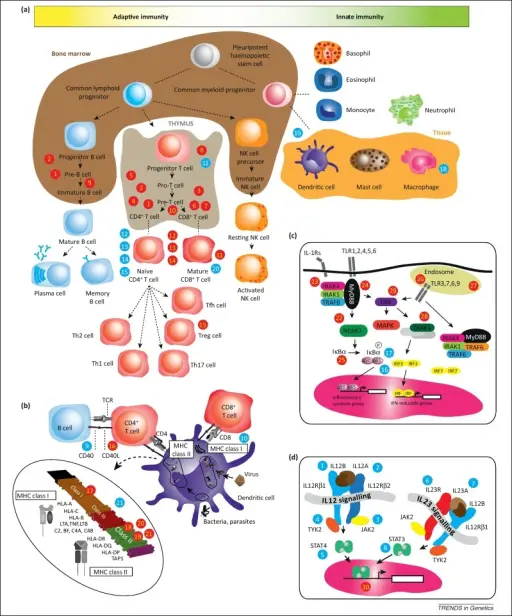
Immunodeficiencies associated with systemic diseases are those that are born with and that affect the entire body. Examples of immunodeficiencies associated with systemic diseases include Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome and ataxia telangiectasia.