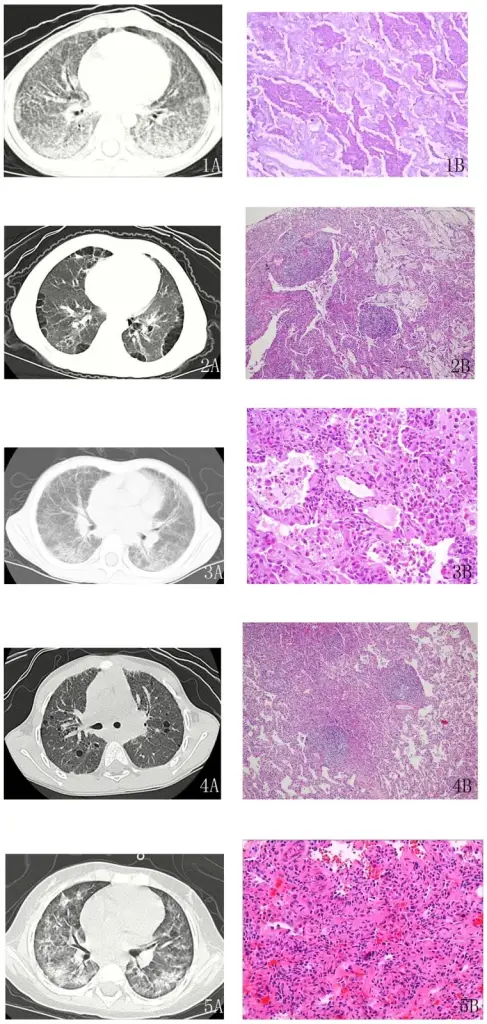
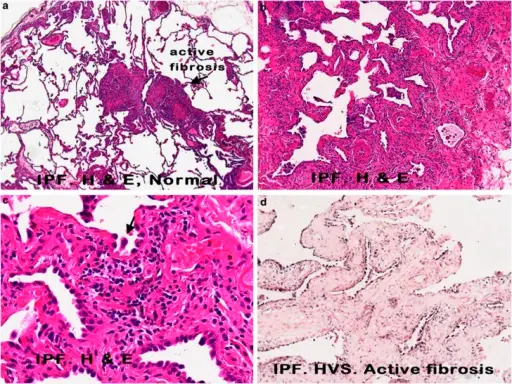
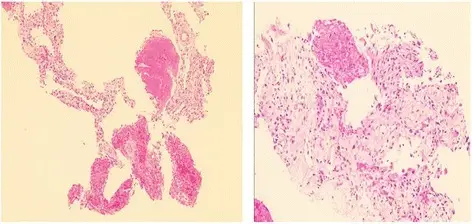
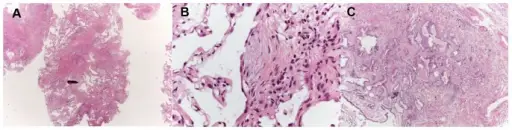
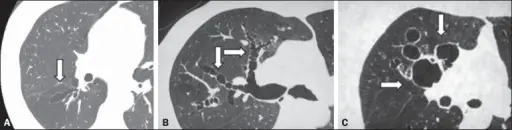
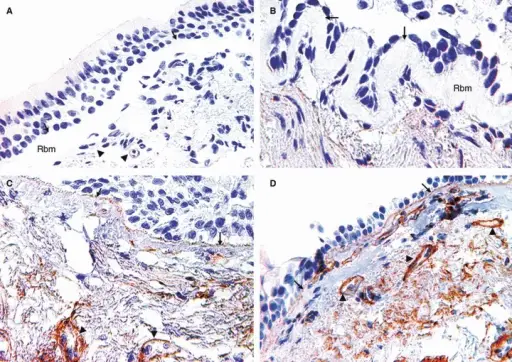
What is Nonspecific Interstitial Pneumonia?
Nonspecific Interstitial Pneumonia is an anomaly that could not be classified into one of the idiopathic interstitial pneumonia types. What is the Pathology of Nonspecific Interstitial Pneumonia? The pathology of nonspecific interstitial pneumonia is: -Etiology: The cause of nonspecific interstitial…