What is Myotonic Dystrophy?
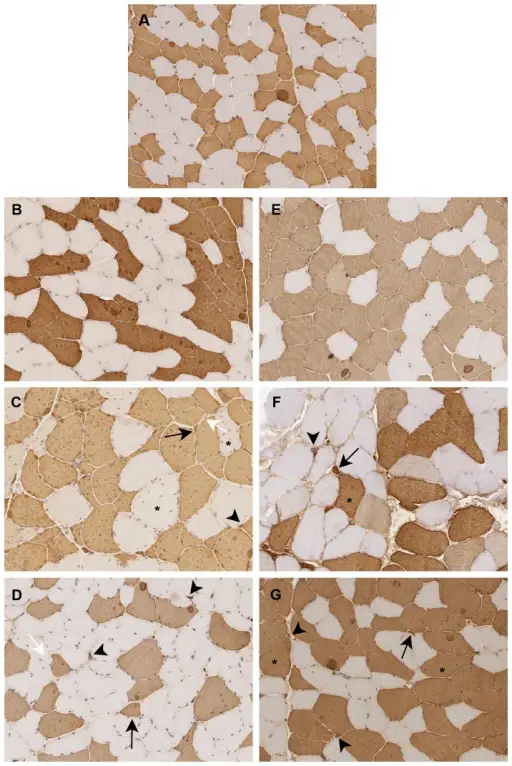
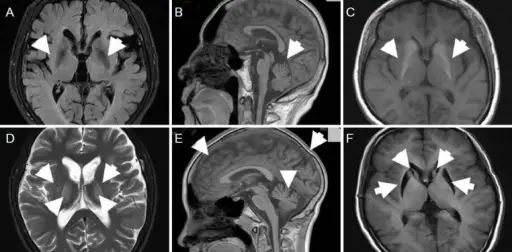
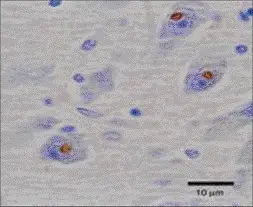
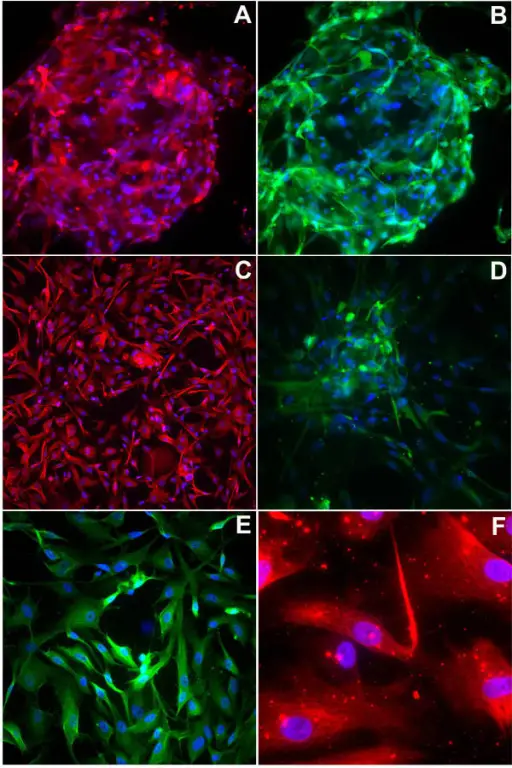
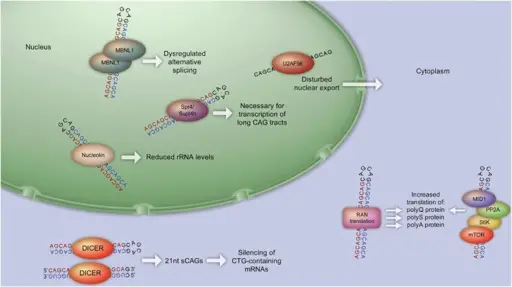
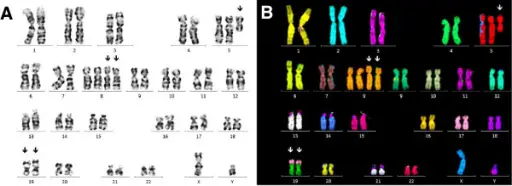
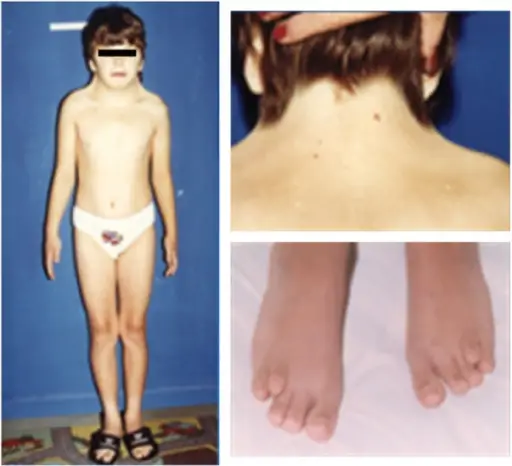
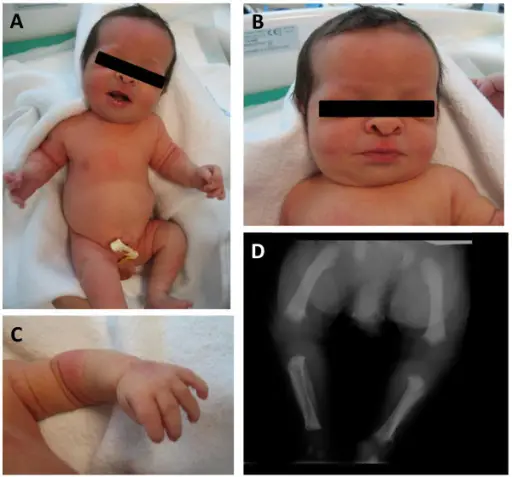
Myotonic dystrophy is a type of muscular dystrophy, a group of genetic disorders that cause progressive muscle loss and weakness. What is the Pathology of Myotonic Dystrophy? The pathology of myotonic dystrophy is: -Etiology: The microsatellite expansion responsible for DM1…