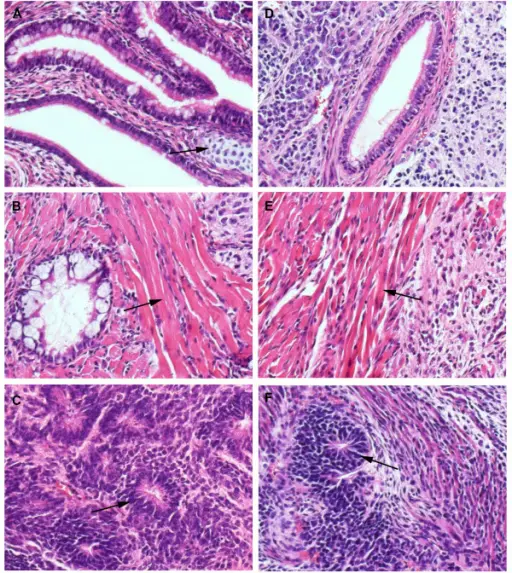
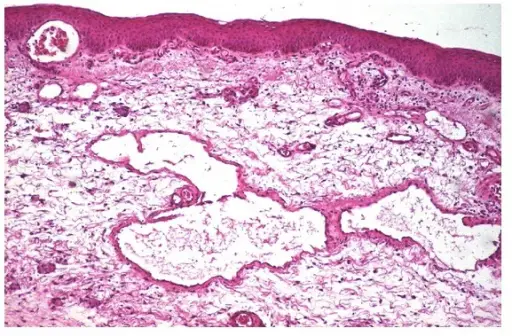
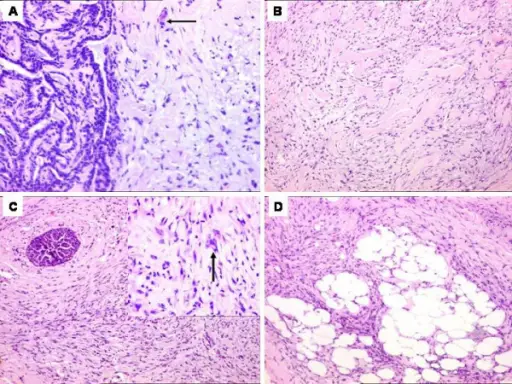
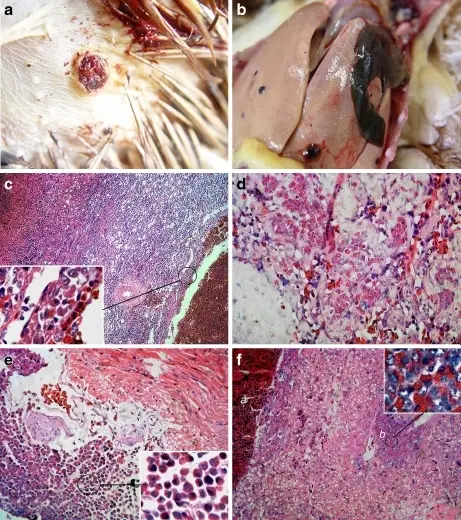
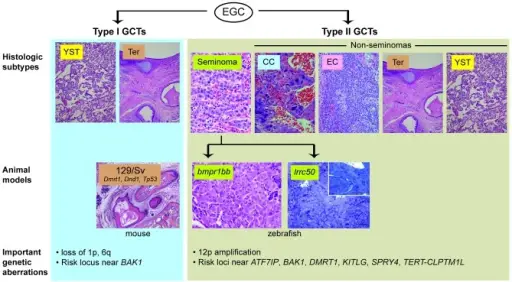
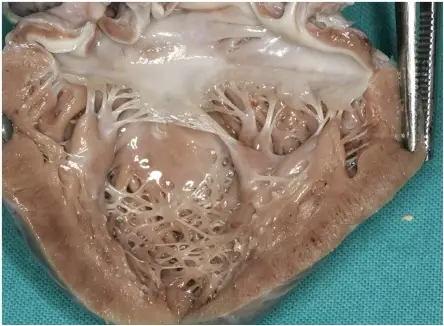
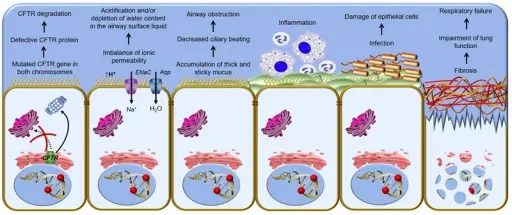
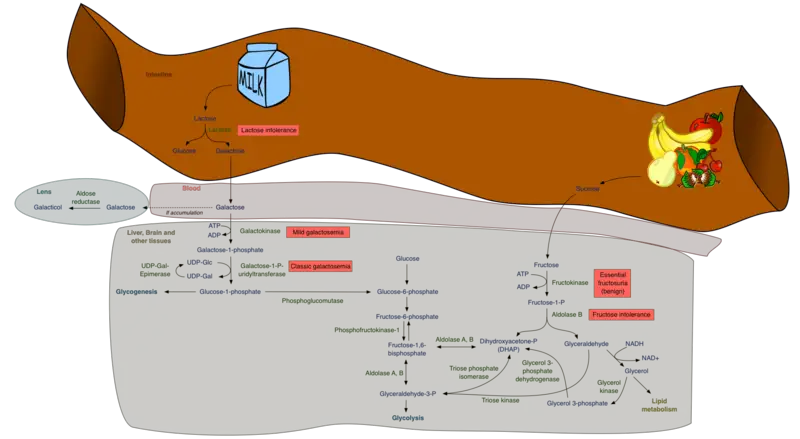
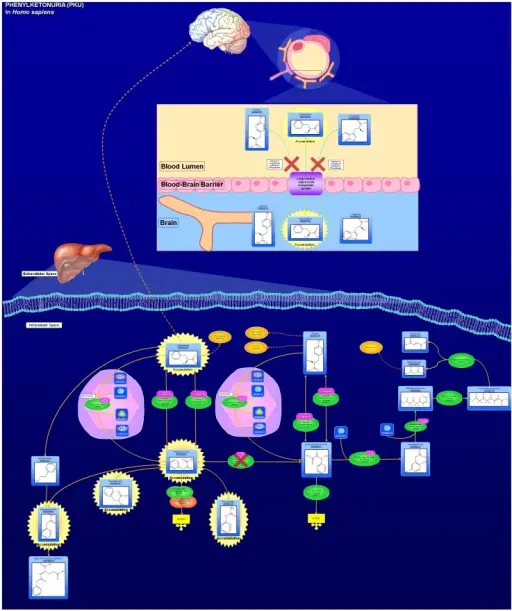
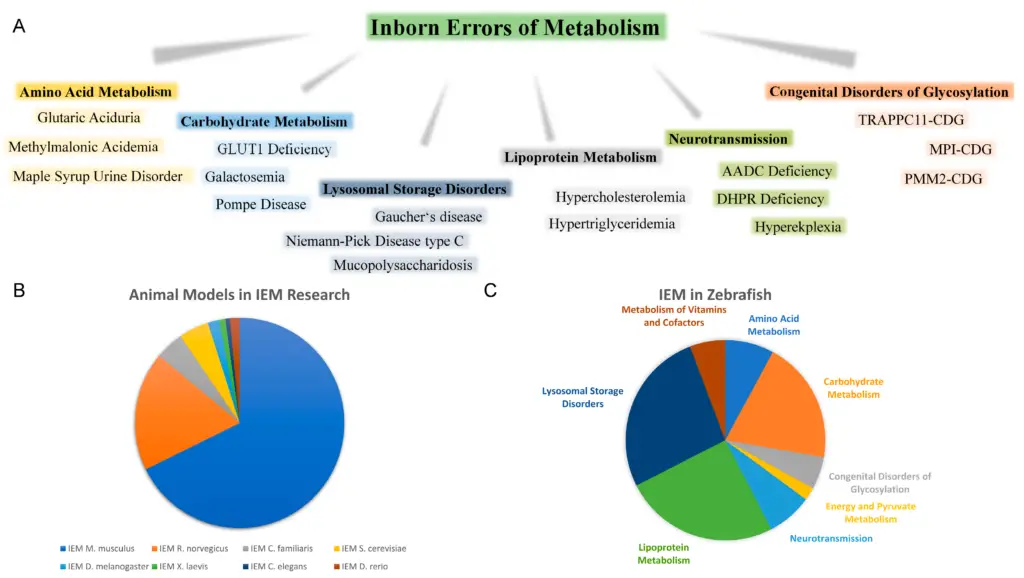
What are Teratomas?
Teratomas are rare tumors that may hold different types of tissue such as bone, teeth, muscle, and hair. Teratomas are mostly found in the ovaries, testicles, and sacrum (tailbone), but also sometimes grow in the nervous system and abdomen. A…