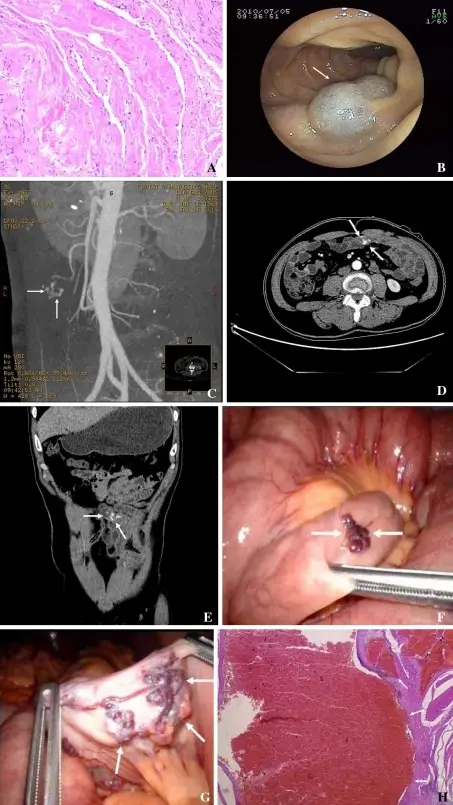
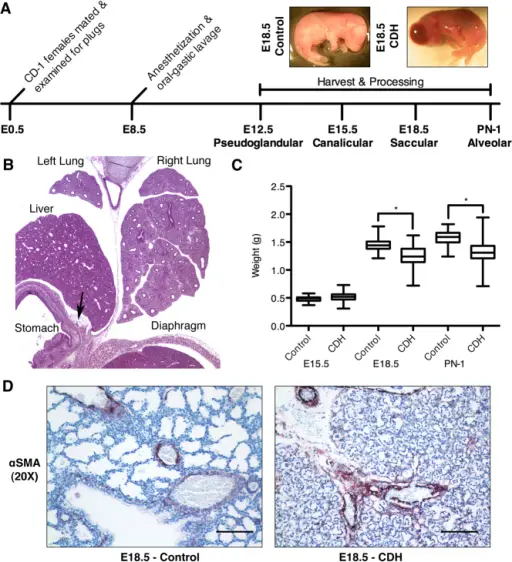
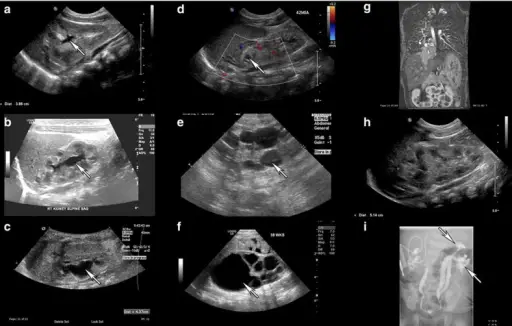
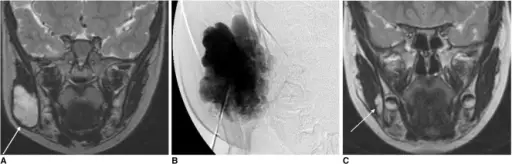
What is a Sequence?
A sequence is one or more secondary morphologic anomalies known or presumed to cascade from a single malformation, disruption, dysplasia, or deformation. The classic example of a sequence is Potter’s syndrome aka oligohydramnios sequence.