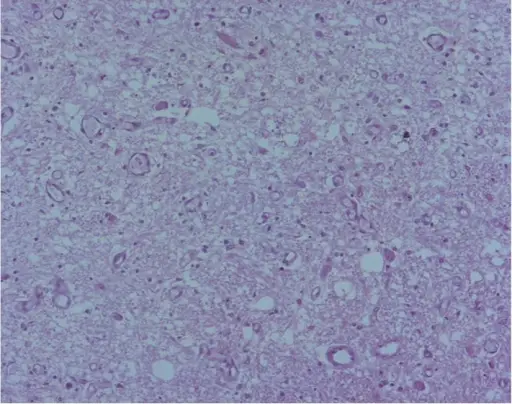
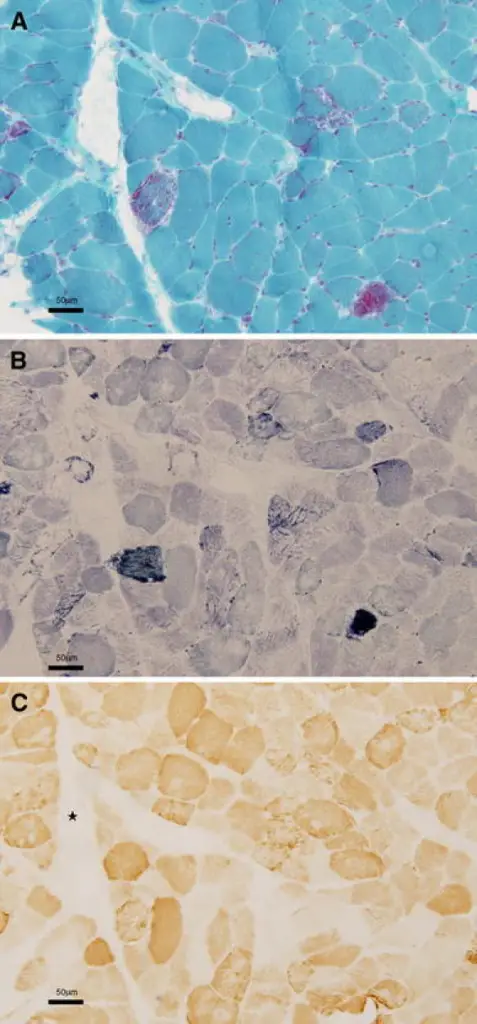
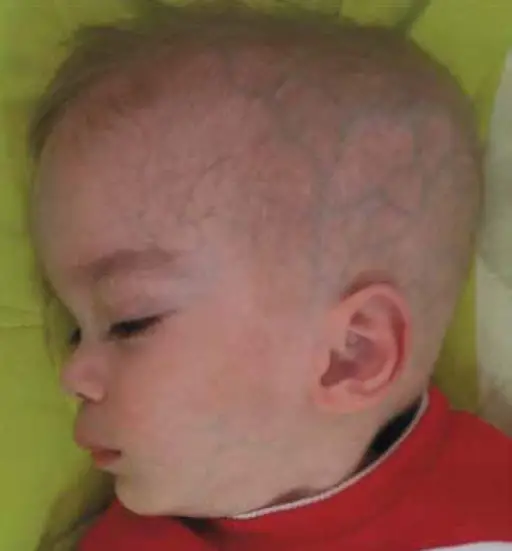
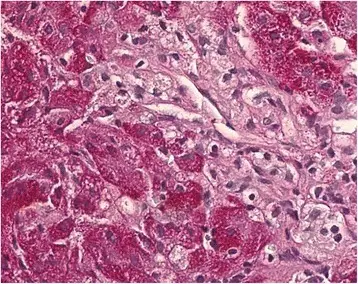
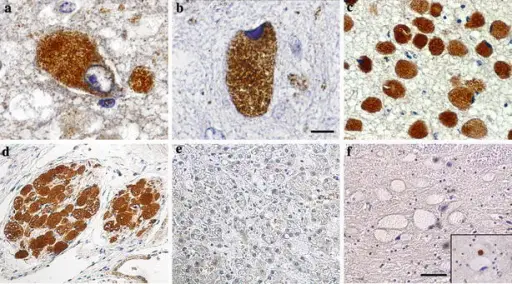
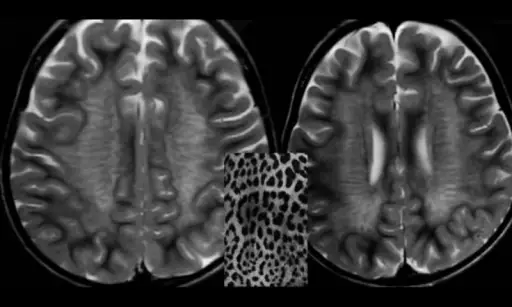
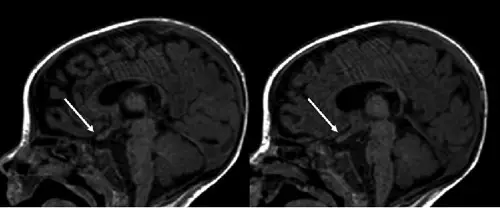
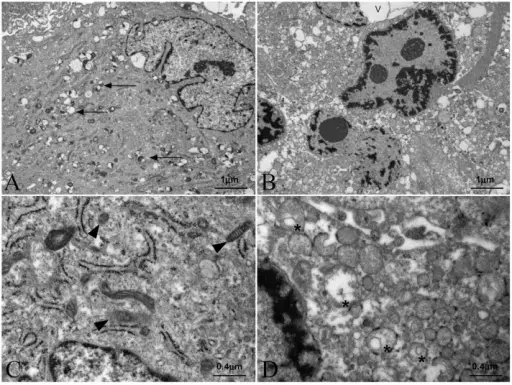
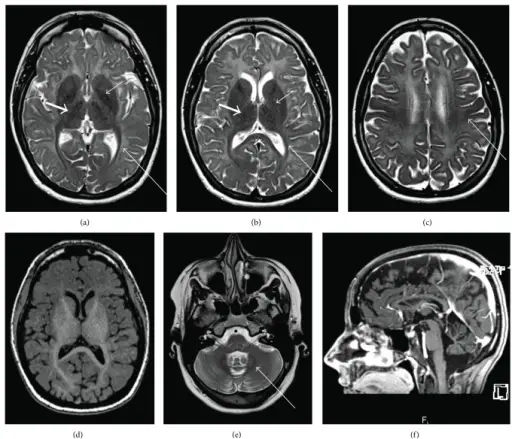
What is Leigh Syndrome?
Leigh syndrome is a rare genetic neurometabolic disorder that is characterized by the degeneration of the central nervous system. What is the Pathology of Leigh syndrome? Etiology: The cause of Leigh syndrome is mutation in mitochondrial DNA or by deficiencies…