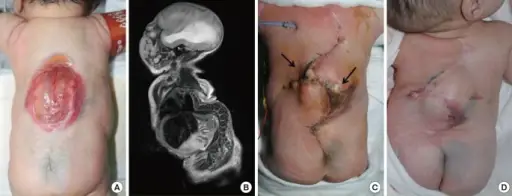
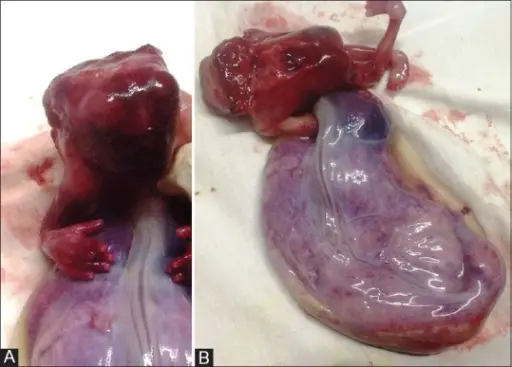
What is Joubert Syndrome?
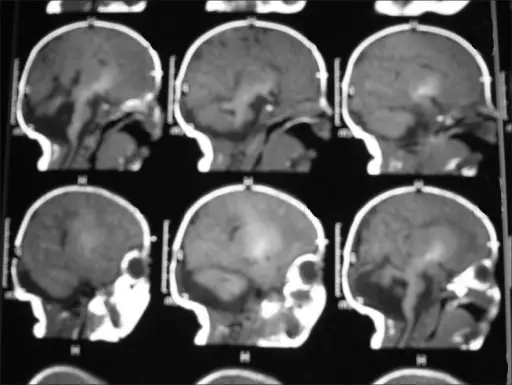
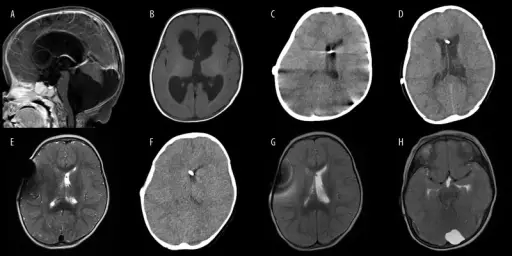
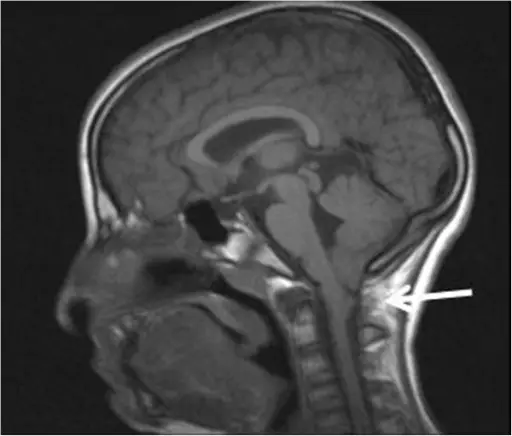
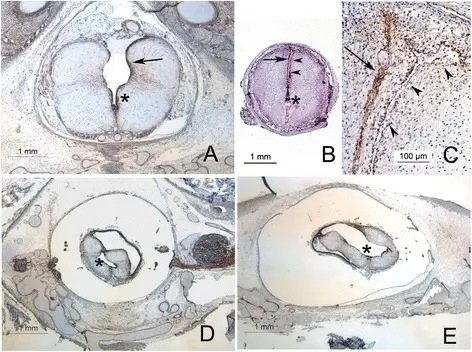
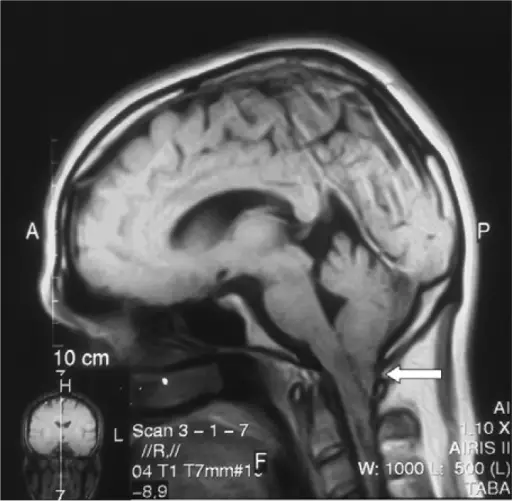
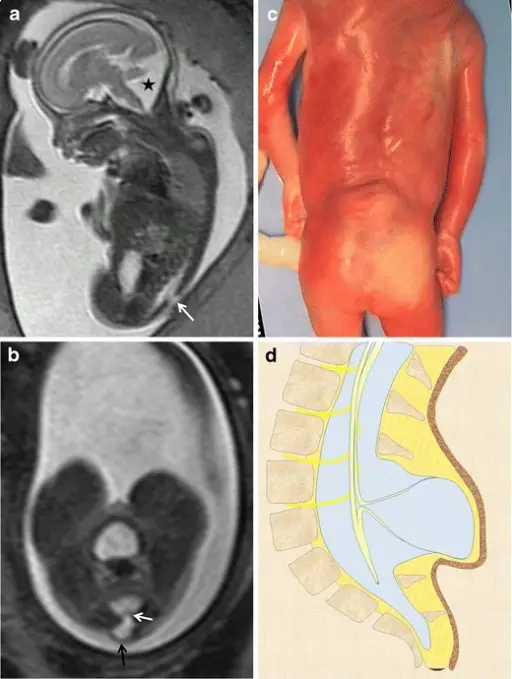
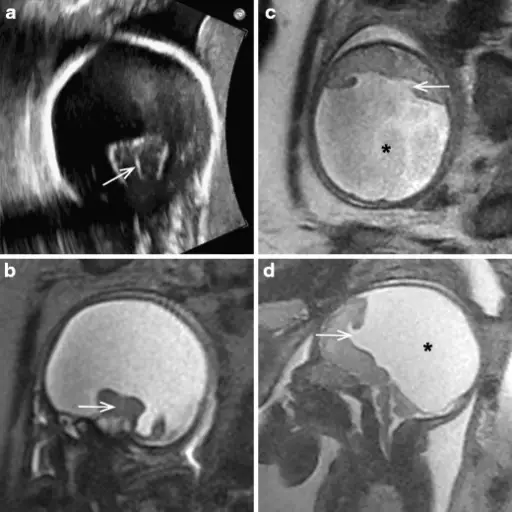
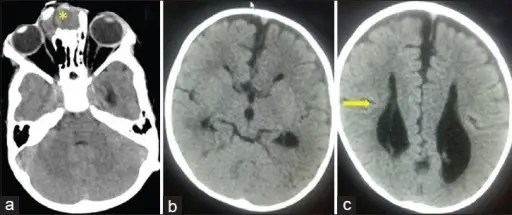
Joubert syndrome is a rare, autosomal recessive congenital cerebellar ataxia characterized by congenital malformation of the brainstem and agenesis or hypoplasia of the cerebellar vermis. What is the Pathology of Joubert Syndrome? Etiology: The cause of Joubert syndrome is an…