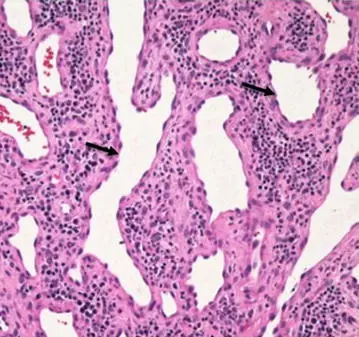
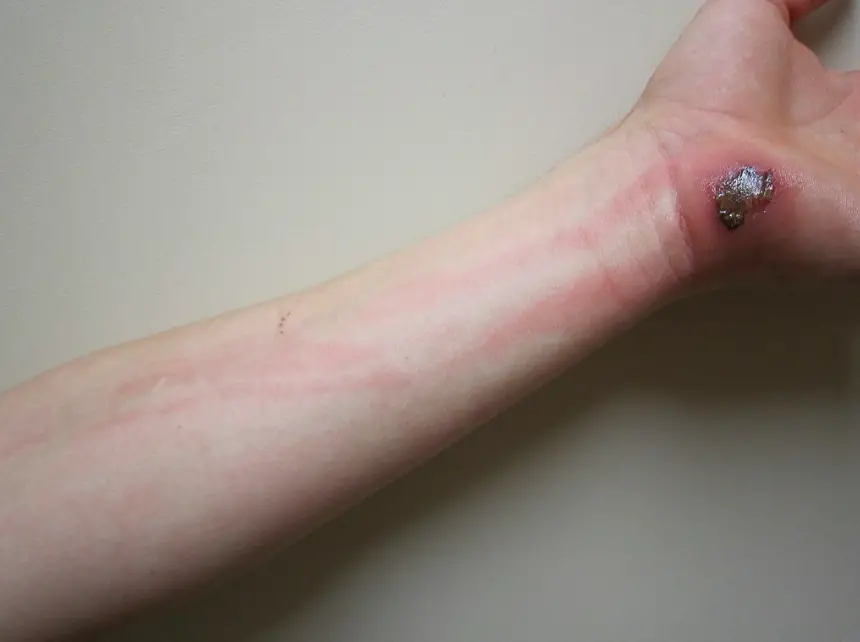
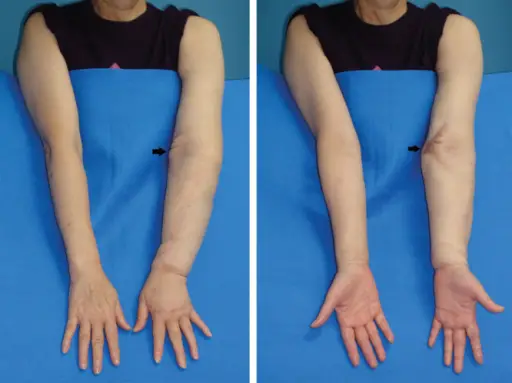
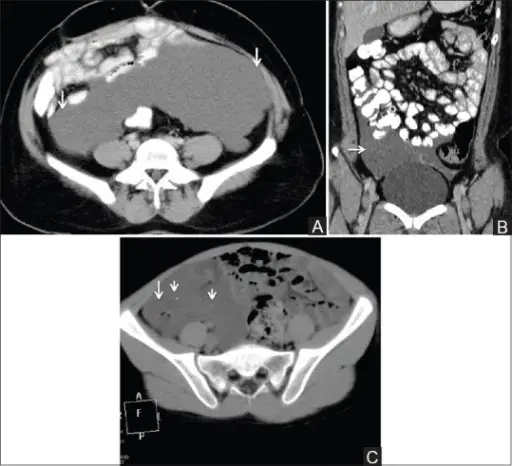
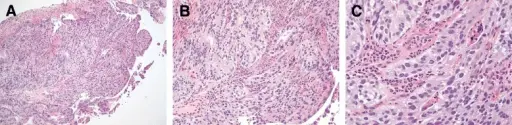
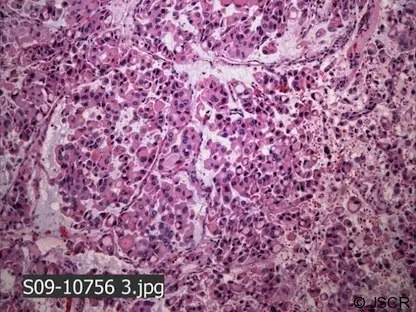
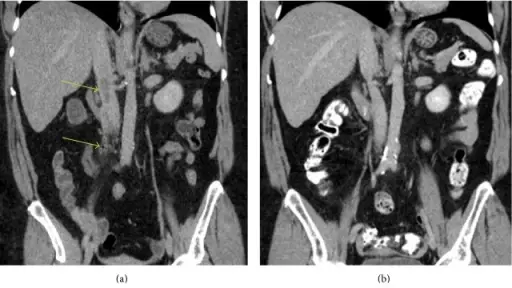
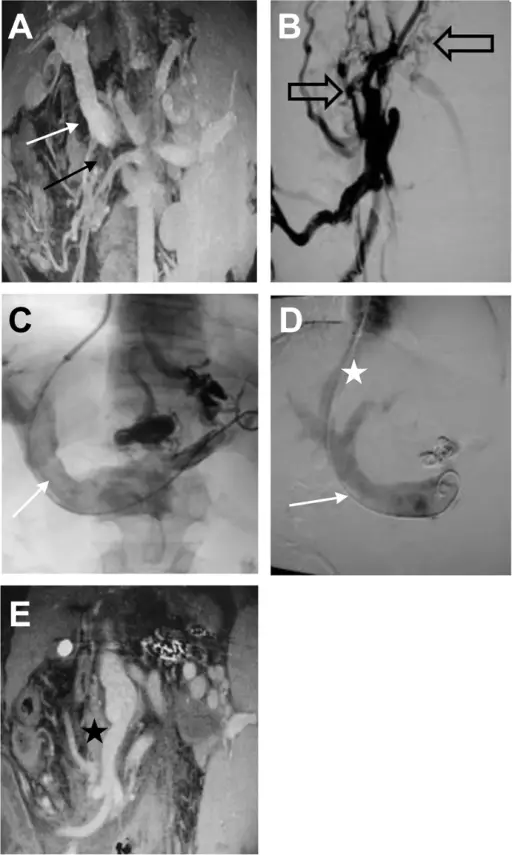
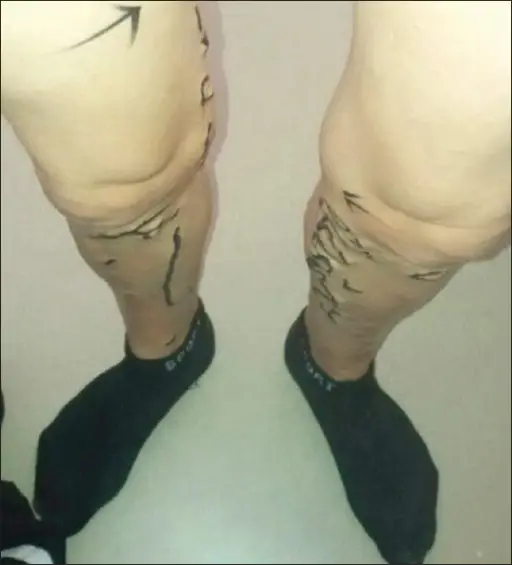
What are Vascular Tumors?
Vascular tumors are a spectrum from the benign hemangiomas, infrequently metastasized intermediate lesions, to fairly rare, highly malignant lesions. Examples of vascular tumors include: Benign tumors and tumor-like lesions of the vasculatureBorderline tumors of the vasculatureMalignant tumors of the vasculature