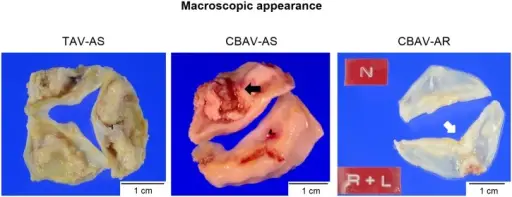
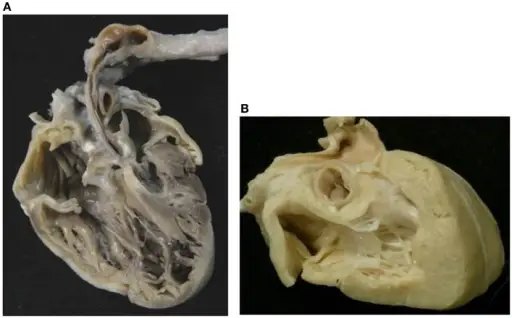
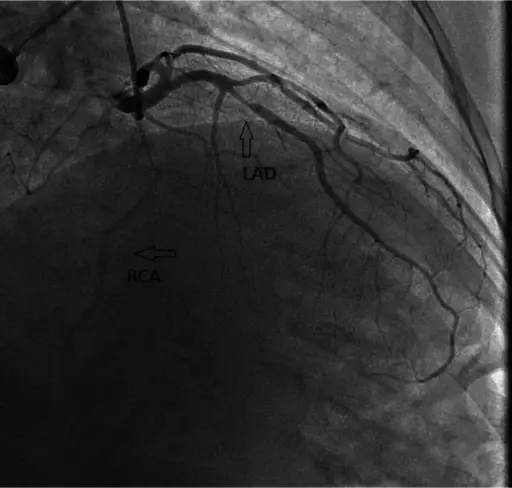
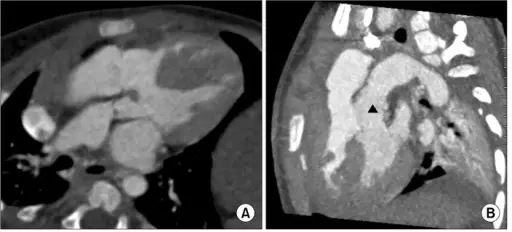
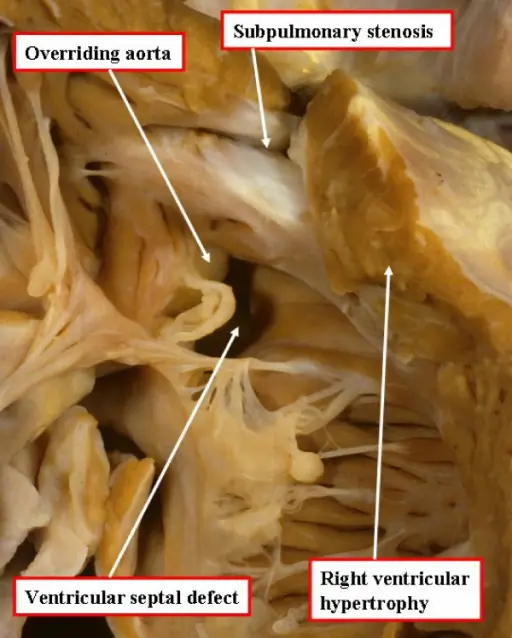
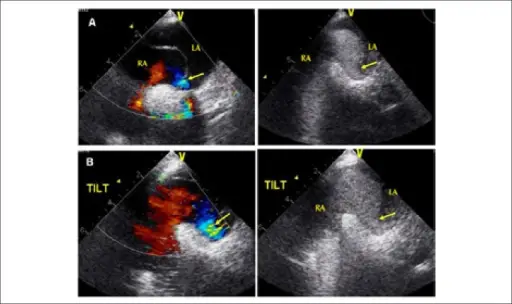
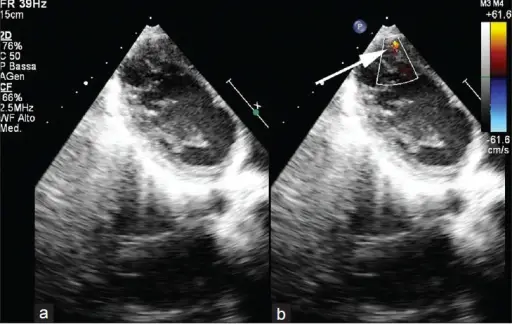
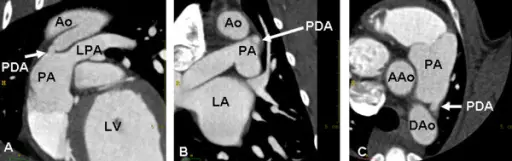
What is Aortic Stenosis?
Aortic stenosis is the narrowing of the aortic valve, reducing or blocking blood flow from the heart to the body. What is the Pathology of Aortic Stenosis? Aortic stenosis pathology includes narrowing of the aortic valve in the valvular, subvalvular,…