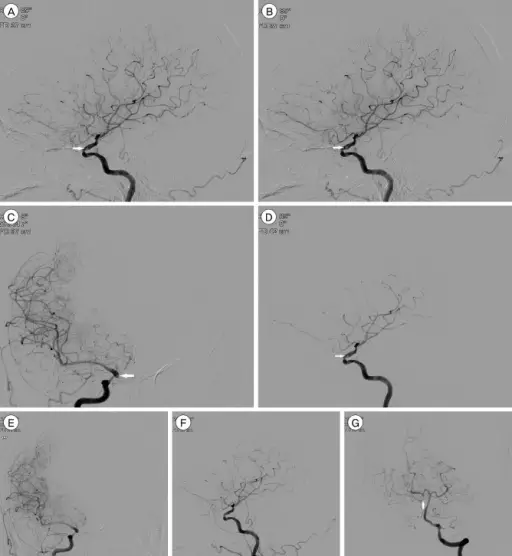
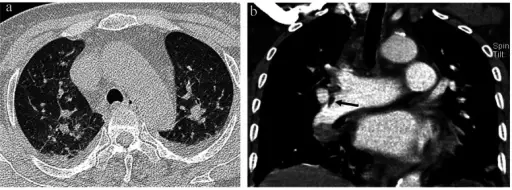
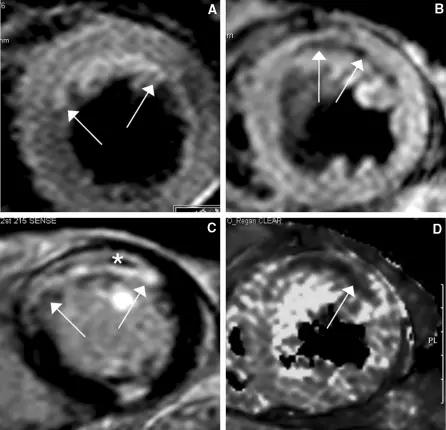
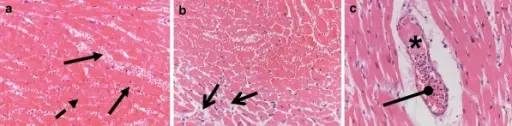
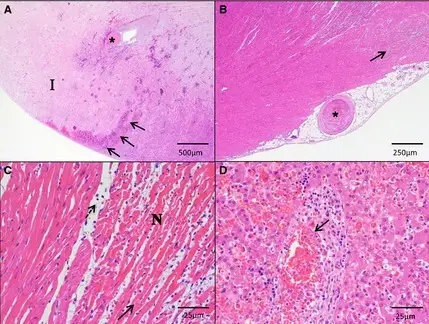
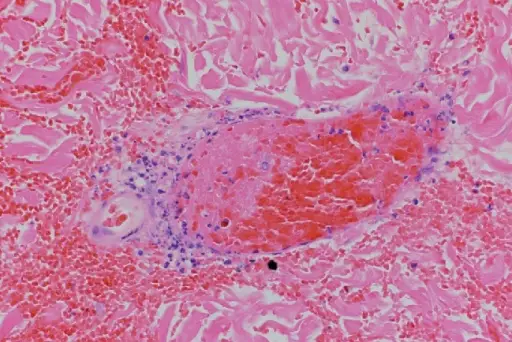
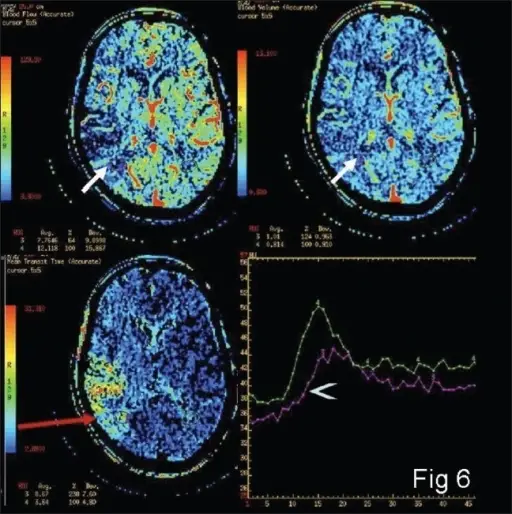
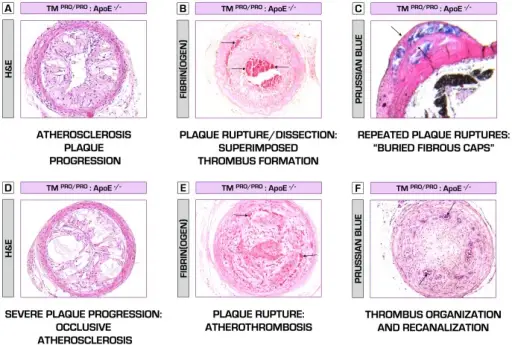
What is Gas Embolism?
Gas embolism occurs when air travels through the vascular system. It can occur in decompression sickness (the bends) when divers ascend too quickly. It can also (very rarely) occur if air enters the arterial or venous system through surgery or…