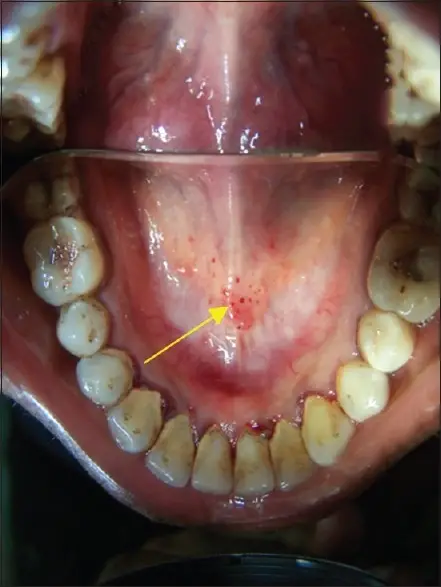
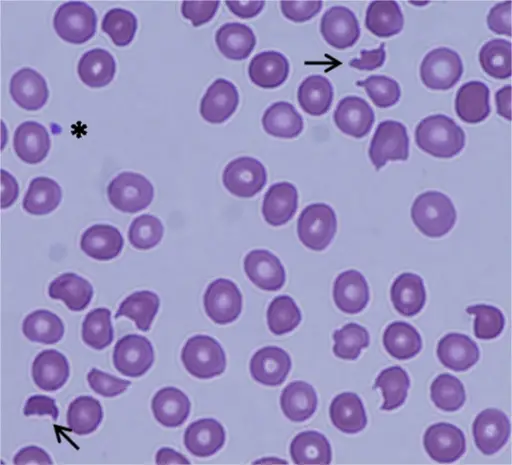
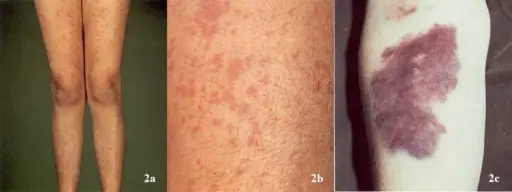
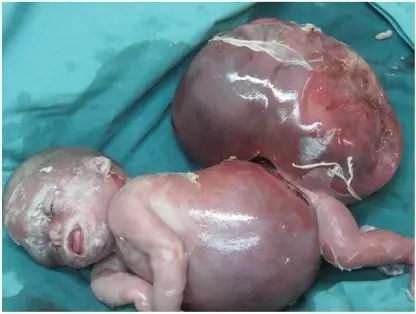
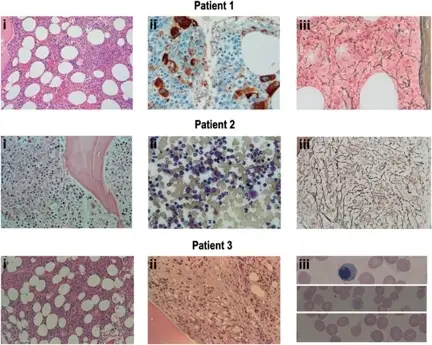
What is Drug Induced Thrombocytopenia?
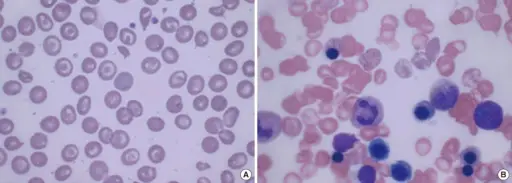
Drug induced thrombocytopenia is a disorder linked to immunologically mediated destruction of platelets after drug ingestion. What is the Pathology of Drug Induced Thrombocytopenia? The pathology of drug induced thrombocytopenia is: -Etiology: The cause of drug induced thrombocytopenia is certain…