Arteriosclerosis, Aortic Dissection and Aneurysm Pathology Study Guide
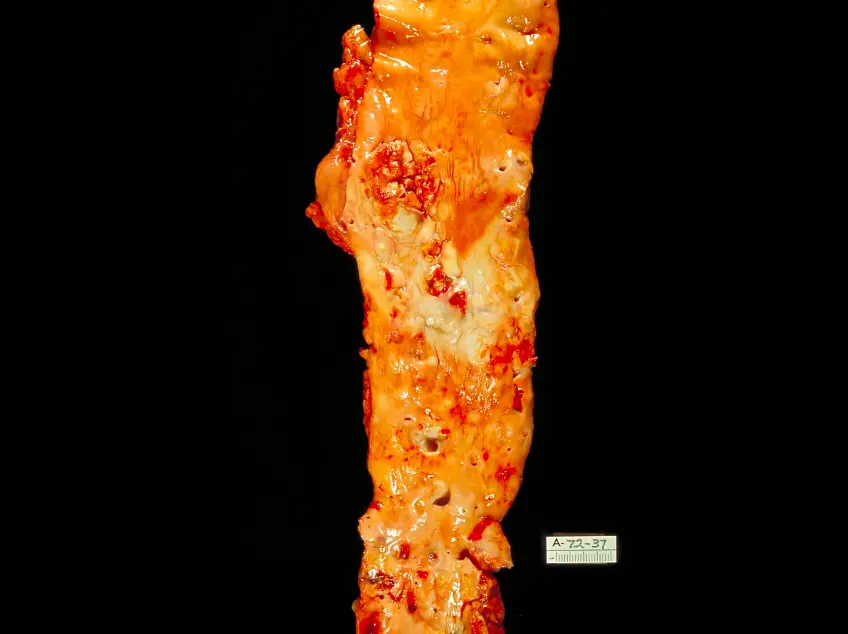
Arteriosclerosis, Aortic Dissection, and Aneurysm Pathology Video Arteriosclerosis Arteriosclerosis is due to the blood artery wall thickening, literally "hard arteries." The types of arteriosclerosis include: Atherosclerosis (hardening and narrowing of large arteries) Arteriolosclerosis (hardening and calcification of small arteries) Mönckeberg…