Thyroid Gland Pathology Study Guide
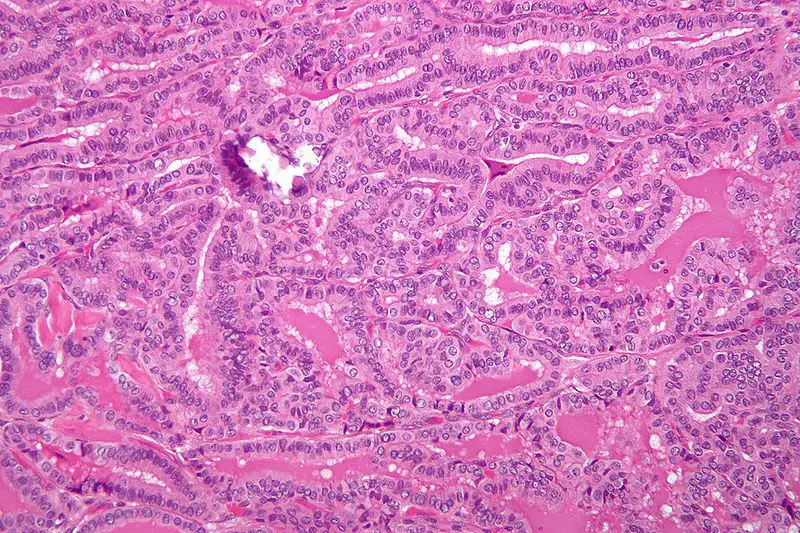
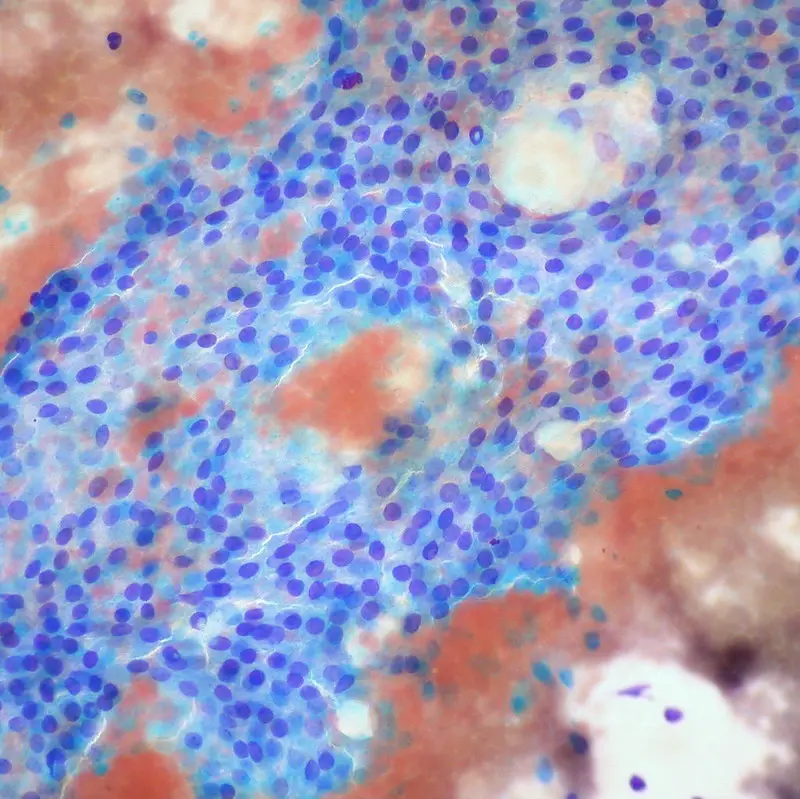
Thyroid Gland Pathology Video Thyroid gland pathology includes: Thyroglossal duct cyst Lingual thyroid Hyperthyroidism Graves' disease Multinodular goiter Cretinism Myxedema Hashimoto thyroiditis Subacute granulomatous thyroiditis Riedel fibrosing thyroiditis Follicular thyroid adenoma Follicular thyroid carcinoma Papillary thyroid carcinoma Medullary thyroid carcinoma…