Hemostasis Pathology Study Guide
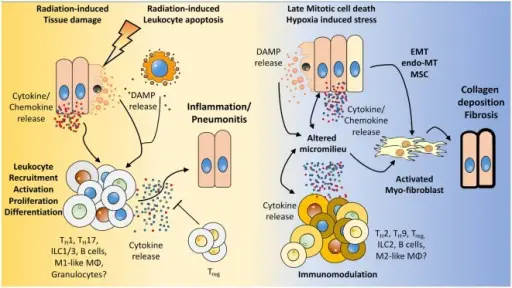
Hemostasis Hemostasis Pathology Video The body's natural response to an injury that stops the bleeding and fixes the damage is known as hemostasis. Blood must be able to flow freely through blood vessels in order to reach tissues. Hemostasis, which…