Exophytic papillomas of the bladder are an uncommon benign exophytic neoplasm composed of a delicate fibrovascular core covered by normal-appearing urothelium.
What is the Pathology of Exophytic Papillomas of the Bladder?
The pathology of exophytic papillomas of the bladder is:
-Etiology: The cause of exophytic papillomas of the bladder is unknown.
-Genes involved: KRAS / HRAS.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to exophytic papillomas of the bladder is encountered as a de novo lesion (without prior urothelial neoplasm).
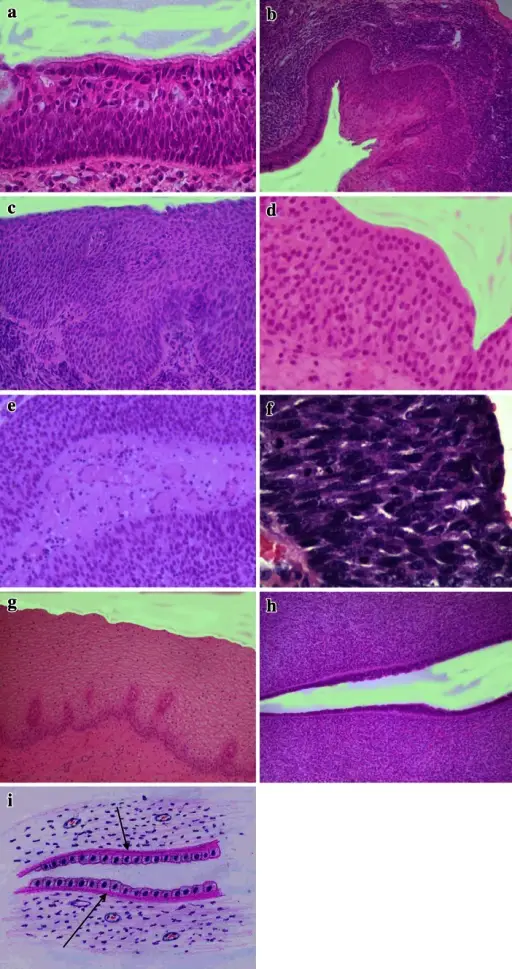
-Morphology: The morphology associated with exophytic papillomas of the bladder shows soft, pink, small isolated growth with delicate papillary structures, usually pedunculated.
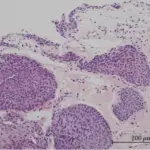
-Histology: The histology associated with exophytic papillomas of the bladder shows discrete papillary structures with central fibrovascular cores with hierarchical branching patterns but without fusion.
How does Exophytic Papillomas of the Bladder Present?
Patients with exophytic papillomas of the bladder typically affect males at less than 50 years of age. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with exophytic papillomas of the bladder include painless hematuria which can either be gross or microscopic.
How is Exophytic Papillomas of the Bladder Diagnosed?
Exophytic papillomas of the bladder are diagnosed by ultrasound, cystoscopy, and biopsy.
How are Exophytic Papillomas of the Bladder Treated?
Exophytic papillomas of the bladder are treated by resection such as transurethral resection of bladder tumor (TURBT).
What is the Prognosis of Exophytic Papillomas of the Bladder?
The prognosis of exophytic papillomas of the bladder is fair.