Inverted papilloma of the bladder is a rare non-invasive endophytic urothelial tumor of the urinary bladder accounting for less than 1% of urothelial neoplasms.
What is the Pathology of Inverted Papilloma of the Bladder?
The pathology of Inverted papilloma of the bladder is:
-Etiology: The etiology of inverted urothelial papilloma of the bladder remains unknown.
-Genes involved: FGFR.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to Inverted papilloma of the bladder is the finding of nonrandom inactivation of X chromosomes is well documented which suggests that inverted papilloma is a clonal neoplasm that arises from a single progenitor cell.
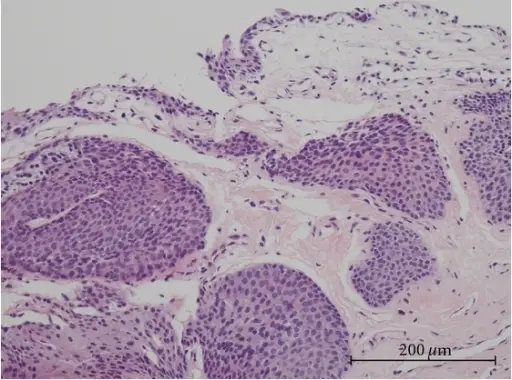
-Morphology: The morphology associated with inverted papilloma of the bladder shows solitary, smooth, polypoid, sessile, or pedunculated. Usually, 3 cm or less but can be as large as 8 cm.
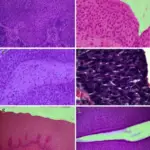
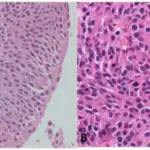
-Histology: The histology associated with inverted papilloma of the bladder shows normal urothelial lining, uniformity of urothelial cells, absent or infrequent mitosis, microcyst formation, and squamous metaplasia.
How does Inverted Papilloma of the Bladder Present?
Patients with inverted papilloma of the bladder typically affect males 5 times more than females in 50 to 60 years of age. The clinical features of inverted urothelial papilloma of the bladder are not specific but may include dysuria, flank pain, low back pain, occasional pyuria, or vague abdominal discomfort.
How is Inverted Papilloma of the Bladder Diagnosed?
Inverted papilloma of the bladder is diagnosed by imaging studies or cystoscopy during the evaluation of other conditions like benign prostatic hyperplasia, hematuria, or prostate cancer. Although ultrasonography of the bladder may detect a bladder mass, cystoscopy remains the diagnostic procedure of choice.
How is Inverted Papilloma of the Bladder Treated?
Inverted papilloma of the bladder is treated by simple excision which is curative.
What is the Prognosis of Inverted Papilloma of the Bladder?
The prognosis of inverted urothelial papilloma is fair depending upon intervention.