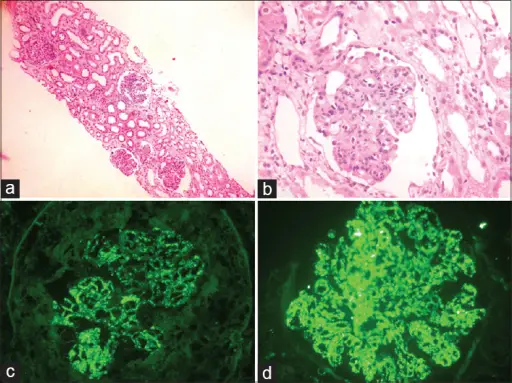
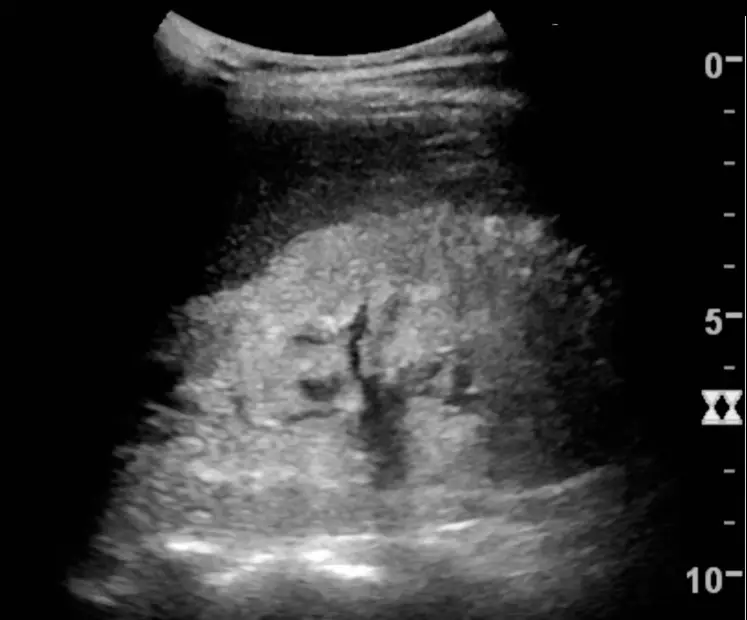
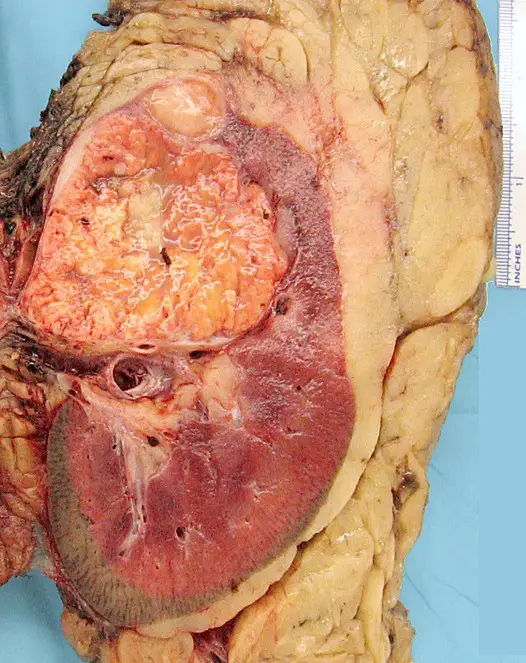
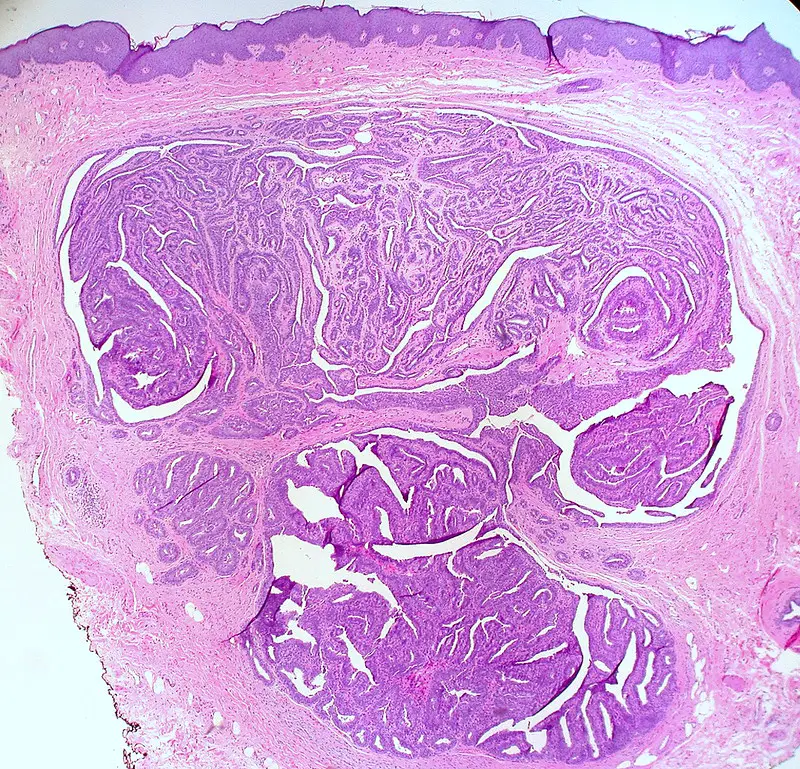
Congenital Heart Defects Pathology Study Guide
Congenital Heart Defects Pathology Video Congenital Heart Defects Congenital heart defects occur throughout embryogenesis (usually weeks 3 through 8). Congenital heart defects are observed in 1% of live births. Most congenital heart defects are incidental and not clinically significant. Congenital…