Thymus pathology is diseases or conditions that may occur to the thymus. Thymic pathology includes congenital issues, cysts, and oncological diseases.
What are Developmental Disorders of the Thymus?
Developmental disorders of the thymus include:
- Thymic aplasia
- Thymic hypoplasia
- Thymic cysts
What is Thymic Aplasia?
Thymic aplasia is the absence of thymic tissue.
What is the Pathology of Thymic Aplasia?
The pathology of thymic aplasia is:
-Etiology: The cause of thymic hypoplasia is a an abnormality that results in the lack of thymic tissue.
-Genes involved: 22q11.2 deletion
-Histology: Lack of thymic tissue.
How does Thymic Aplasia Present?
Patients with thymic aplasia typically present as newborn infants.
How is Thymic Aplasia Diagnosed?
Thymic aplasia is diagnosed by physical exam, and ultrasound.
How is Thymic Aplasia Treated?
Thymic aplasia is treated by thymus transplantation.
What is the Prognosis of Thymic Aplasia?
The prognosis of Thymic aplasia is poor due to the susceptibility of recurrent infectious disease disorders.
What is Thymic Hypoplasia?
Thymic hypoplasia is a condition in which the thymus is underdeveloped or involuted.
What is the Pathology of Thymic Hypoplasia?
The pathology of thymic hypoplasia is:
-Etiology: The cause of thymic hypoplasia may be due to genetic disorders or birth defects.
-Genes: PAX1, TBX1, TBX2
-Pathogenesis: Lack of development and maturation of thymic tissue. This results in immature T cells from the bone marrow not being able to properly mature, which may lead to susceptibility to infections.
-Histology: Unremarkable thymic tissue.
How does Thymic Hypoplasia Present?
Patients with thymic hypoplasia typically present in immature infants. Underdevelopment of the thymus results in an increased infection risk.
How is Thymic Hypoplasia Diagnosed?
Thymic hypoplasia is diagnosed by physical exam and ultrasound.
How is Thymic Hypoplasia Treated?
Thymic hypoplasia is treated by immuno-precautions.
What are Thymic Cysts?
Thymic cysts are cysts that occur involving thymic tissue.
What is the Pathology of Thymic Cysts?
The pathology of thymic cysts is:
-Etiology: The cause of thymic cyst can be either acquired or congenital.
-Morphology: Enlarged lump in neck or sternal region.
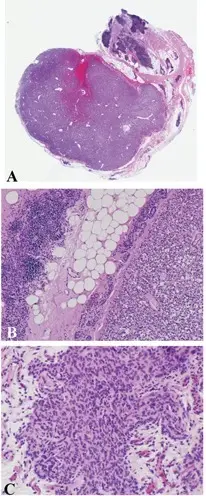
-Histology: Thin walled cysts composed of bland cells and thymic tissue. Hassal corpuscles may be present.
How does Thymic Cysts Present?
Thymic cysts are typically discovered early in life, and mostly affect males.
How are Thymic Cysts Diagnosed?
Thymic cysts are diagnosed with physical exam, ultrasound, and biopsy.
How are Thymic Cysts Treated?
Thymic cysts are treated surgically.
What is the Prognosis of Thymic Cysts?
The prognosis of thymic cysts is good.
What is Thymic Hyperplasia?
Thymic hyperplasia is increased thymic tissue.
What is the Pathology of Thymic Hyperplasia?
The pathology of thymic hyperplasia is:
-Etiology: The cause of thymic hyperplasia may be stress, medication use, endocrine disorders, or tumor.
-Pathogenesis: Increased thymic cells.
-Morphology: Increased size of thymus.
-Histology: Cellular thymocytes.
How does Thymic Hyperplasia Present?
Patients with thymic hyperplasia are typically children of either gender. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with thymic hyperplasia are not remarkable.
How is Thymic Hyperplasia Diagnosed?
Thymic hyperplasia is diagnosed by physical exam, imaging, and biopsy.
How is Thymic Hyperplasia Treated?
Thymic hyperplasia may resolve on its own, or be treated surgically.
What is the Prognosis of Thymic Hyperplasia?
The prognosis of thymic hyperplasia is good.
What is a Thymoma?
Thymomas are neoplasms of the thymus of thymic epithelial origin. Thymomas may be benign or malignant.
What are the Types of Thymomas?
The specific types of thymomas include:
- Type A
- Atypical A
- Type AB
- Type B1
- Type B2
- Type B3
- MNT
- Metaplastic Thymoma
Note that the letters in the types indicate the types of neoplastic cells that are present:
- A = Spindled
- B = Polygonal
What is the Pathology of Thymomas?
The pathology of thymomas is:
-Etiology: The cause of thymoma is unknown.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to thymoma is proliferation of thymic epithelial cells.
-Histology: Thymomas tend to have lobulated or bosselated architecture. The cellular lobules are complosed of spindled or polygonal neoplastic epithelial cells and reactive thymocytes that are intersected with fibrous bands.
How do Thymomas Present?
Patients with thymomas are typically in their fifties, and there is no sexual or racial associated risks.
How are Thymomas Diagnosed?
Thymomas are diagnosed by physical exam, imaging, and biopsy.
How is Thymoma Treated?
Thymomas are treated by surgical resection.
What is the Prognosis of Thymoma?
The prognosis of thymomas is generally good if diagnosed and treated early.